- Factors to Consider When Choosing Health Insurance
- Types of Health Insurance Plans
- Key Features to Look for in Health Insurance
- Top Health Insurance Companies
- Tips for Finding the Right Health Insurance Plan
- Understanding Health Insurance Terminology
- Final Wrap-Up: What Are Good Health Insurance Companies
- Clarifying Questions
What are good health insurance companies? It’s a question that pops up every time you need to pick a plan. Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like a maze, with confusing terms and a ton of choices. But, don’t worry, you’re not alone! This guide breaks down everything you need to know to find the best health insurance for your situation.
From understanding your needs to comparing plans, we’ll walk you through the process step-by-step. So, grab a comfy chair, get ready to learn, and let’s get you covered!
Factors to Consider When Choosing Health Insurance

Choosing the right health insurance plan is a crucial decision that impacts your financial well-being and access to healthcare. Navigating the complexities of health insurance can be overwhelming, but understanding your individual needs and the various factors involved can help you make an informed choice.
Understanding Your Health Needs and Coverage Requirements
Knowing your individual health needs and coverage requirements is essential when selecting a health insurance plan. Consider your current health status, any pre-existing conditions, and your anticipated healthcare needs in the future. If you have specific medical needs, such as chronic illnesses or frequent doctor visits, you’ll want to prioritize plans that offer comprehensive coverage and access to specialized healthcare providers.
Factors to Consider
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the best health insurance plan for you. Carefully consider the following aspects:
Budget
Your budget is a primary consideration when choosing health insurance. Different plans have varying premiums, deductibles, and copayments, which can significantly impact your out-of-pocket expenses. It’s essential to determine a budget that aligns with your financial capabilities and allows you to afford the necessary healthcare services.
Coverage Options
Health insurance plans offer different coverage options, such as HMOs, PPOs, and POS plans. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of network size, cost, and flexibility. Research and compare these options to understand which best suits your needs and preferences.
Network Size
The size of the insurance plan’s network, which encompasses the healthcare providers and facilities covered, is a critical factor. A larger network provides more choices and potentially better access to specialists and hospitals. However, it’s essential to ensure that your preferred doctors and hospitals are included in the network.
Customer Service
Customer service is crucial when dealing with health insurance. You want a provider that offers responsive and helpful support, particularly during claims processing and when navigating complex medical bills. Look for companies with positive customer reviews and a track record of providing excellent service.
Comparing Plans and Analyzing Pros and Cons
Once you’ve identified key factors, it’s essential to compare plans from multiple providers. This allows you to assess the pros and cons of each option and make an informed decision. Consider factors like premiums, deductibles, copayments, network size, coverage options, and customer service ratings. You can use online tools, insurance brokers, or consult with a financial advisor to compare plans effectively.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like trying to decipher a foreign language. But fear not, we’re here to break down the different types of plans available so you can choose the one that best fits your needs and budget.
When selecting a health insurance plan, you’ll encounter various types, each with its own unique features, benefits, and limitations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial to making an informed decision that aligns with your healthcare preferences and financial situation. Let’s delve into the common types of health insurance plans available, shedding light on their key characteristics and factors that influence their suitability.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs are known for their emphasis on preventative care and cost-effectiveness. They operate under a network system, requiring you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network. Your PCP acts as a gatekeeper, referring you to specialists within the network for further care.
- Lower Premiums: HMOs often have lower monthly premiums compared to other plan types.
- Limited Network: You are typically restricted to seeing providers within the HMO’s network. This can limit your choice of doctors and hospitals.
- Pre-authorization: Many HMOs require pre-authorization for certain services and procedures, meaning you’ll need to get approval from your insurance company before receiving care.
- Emphasis on Preventative Care: HMOs often encourage preventative care services, such as annual checkups and screenings, with minimal or no out-of-pocket costs.
- Co-pays: You typically pay a fixed co-pay for each doctor visit or service, which can be significantly lower than out-of-pocket expenses with other plans.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to see doctors both in and out of the network. However, you’ll pay higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care.
- Higher Premiums: PPOs generally have higher monthly premiums compared to HMOs due to the wider network and greater flexibility.
- Larger Network: PPOs offer a wider network of doctors and hospitals, giving you more options for care.
- No PCP Required: You don’t need a primary care physician to access specialists in a PPO. This allows for greater freedom in choosing healthcare providers.
- Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: While you have more provider options, out-of-pocket expenses for out-of-network care are significantly higher than for in-network care.
- Co-pays and Co-insurance: PPOs often involve a combination of co-pays and co-insurance, meaning you’ll pay a fixed amount for certain services and a percentage of the remaining costs.
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs)
EPOs resemble HMOs in their network limitations, but they differ in their approach to out-of-network care. EPOs typically do not cover out-of-network services at all, except in emergencies.
- Lower Premiums: EPOs generally have lower premiums than PPOs due to their restricted network.
- Limited Network: Similar to HMOs, EPOs have a limited network of providers. You must choose from doctors and hospitals within the network.
- No Out-of-Network Coverage: EPOs typically do not cover out-of-network services, except in emergency situations. This means you’ll be responsible for the entire cost of care if you see a provider outside the network.
- Pre-authorization: EPOs often require pre-authorization for certain services and procedures, similar to HMOs.
Point-of-Service (POS) Plans
POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs, offering a hybrid approach to healthcare. You’ll have a PCP within the network, but you can also access out-of-network providers with higher out-of-pocket costs.
- PCP Required: You need to choose a PCP within the POS network.
- Limited Network: POS plans have a limited network of providers, but you can access out-of-network care.
- Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: Out-of-network care is covered, but you’ll pay higher out-of-pocket expenses compared to in-network care.
- Pre-authorization: POS plans often require pre-authorization for certain services and procedures.
Key Features to Look for in Health Insurance
Choosing the right health insurance plan can be a daunting task, but it’s crucial for your financial well-being and access to quality healthcare. You’ll need to look beyond just the price tag and consider the features that align with your specific needs and priorities.
Essential Coverage
It’s essential to have a plan that covers the services you’re most likely to need. Here are some key areas to consider:
- Preventive Care: Preventive care services like annual checkups, screenings, and immunizations are essential for maintaining good health and catching potential problems early. Look for plans that cover these services without any out-of-pocket costs.
- Prescription Drugs: Many people rely on prescription medications, so it’s important to understand how your plan handles drug coverage. Consider the plan’s formulary (list of covered drugs), copayments, and any restrictions on generic drugs.
- Hospitalization: In case of an unexpected illness or injury, you’ll need coverage for hospital stays, surgery, and other related services. Look for plans with robust coverage for hospitalization and ensure it includes your preferred hospitals.
Financial Considerations
Beyond the coverage, you’ll need to factor in the financial aspects of your plan. Here’s a breakdown of key terms:
- Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts covering costs. A higher deductible generally means lower monthly premiums, but you’ll pay more upfront for medical services. Consider your budget and how often you expect to use healthcare services.
- Copayments: Fixed amounts you pay for specific services, such as doctor visits or prescriptions. Copayments can help manage costs, but they can add up over time.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The maximum amount you’ll pay for covered medical expenses in a year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance will cover the remaining costs. A lower out-of-pocket maximum provides greater financial protection.
Network Size
Your plan’s network determines which doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers are covered. A larger network generally provides more choices and flexibility, but it might come with higher premiums.
- In-Network Providers: These are the doctors and hospitals that have contracts with your insurance company and offer discounted rates. Using in-network providers will generally result in lower out-of-pocket costs.
- Out-of-Network Providers: These providers are not part of your plan’s network, and you’ll likely pay higher costs for their services. If you have a strong preference for a specific out-of-network provider, consider if the potential savings from a smaller network outweigh the added cost.
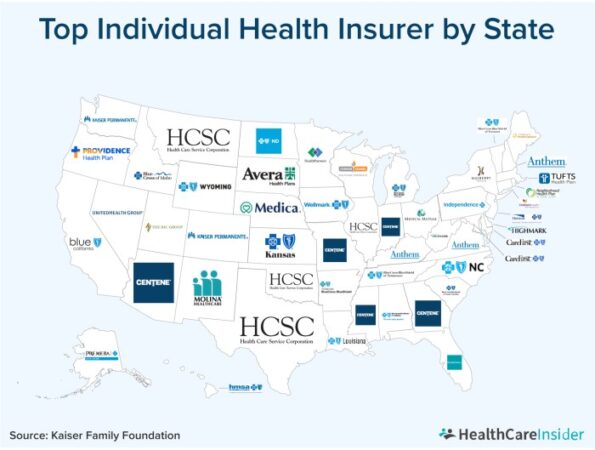
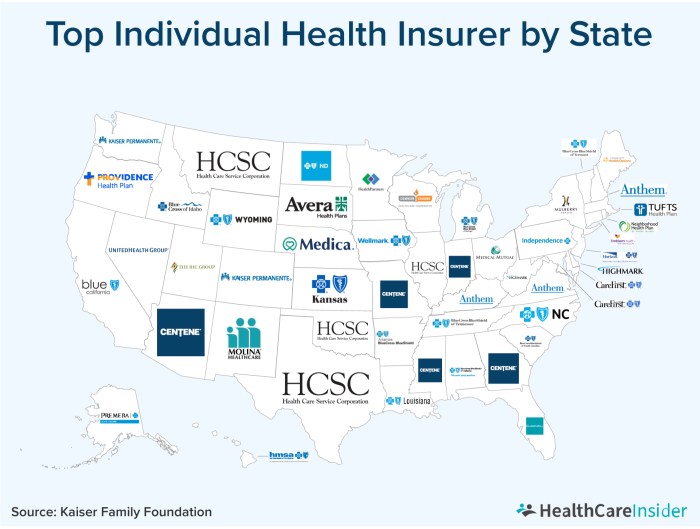
Top Health Insurance Companies

Choosing the right health insurance company can be a daunting task, especially considering the wide range of options available. But don’t worry, we’re here to help you navigate this jungle of coverage! We’ve compiled a list of some of the top health insurance companies based on factors like financial stability, customer satisfaction, and plan offerings. This will help you make an informed decision and find the perfect fit for your health insurance needs.
Top Health Insurance Companies Compared
Here’s a breakdown of some of the leading health insurance companies in the U.S., giving you a glimpse into their strengths and weaknesses:
| Company Name | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue Cross Blue Shield | Wide network coverage, various plan options, strong financial stability | Largest health insurer in the U.S., known for its comprehensive coverage and extensive network | Can be expensive, customer service can vary depending on location |
| UnitedHealthcare | Large network, diverse plan options, innovative healthcare programs | Offers a wide range of plans, including specialized programs for specific health needs | Customer service can be challenging, premiums can be higher than average |
| Anthem | Competitive pricing, robust network, emphasis on preventative care | Known for its competitive pricing and focus on preventive healthcare services | Network coverage may vary depending on location, customer service has received mixed reviews |
| Cigna | Global reach, focus on wellness programs, strong customer service | Offers a global network, known for its commitment to wellness programs and customer satisfaction | May not have the widest network coverage in all areas, premiums can be higher |
| Humana | Specialized plans for seniors, Medicare Advantage plans, strong customer service | Known for its focus on Medicare Advantage plans and senior health needs, generally receives positive customer service reviews | Limited network coverage in some areas, may not be the best option for younger individuals |
Tips for Finding the Right Health Insurance Plan
Navigating the health insurance marketplace can feel like trying to decipher a foreign language, but don’t worry, you’ve got this! Finding the right plan is all about understanding your needs and knowing where to look.
Understand Your Needs
Before diving into the insurance jungle, take a moment to reflect on your health needs and financial situation. Think about your current health status, any pre-existing conditions, and how often you typically visit the doctor. Also, consider your budget and what you can comfortably afford to pay in premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
Understanding Health Insurance Terminology
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a foreign language. It’s filled with terms that sound like they belong in a medical textbook, but understanding them is key to making informed decisions about your coverage. Let’s break down some common health insurance terms and shed some light on their meanings.
Common Health Insurance Terms, What are good health insurance companies
These terms are crucial for understanding the financial aspects of your health insurance plan. Knowing what they mean can help you make informed decisions about your coverage and avoid unexpected costs.
- Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services before your insurance kicks in. For example, if you have a $1,000 deductible, you’ll pay the first $1,000 of medical expenses yourself. After you’ve met your deductible, your insurance will start covering a portion of your costs.
- Copay: A fixed amount you pay for a specific healthcare service, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription. For instance, your copay for a doctor’s visit might be $20, while your copay for a prescription might be $10.
- Coinsurance: The percentage of healthcare costs you pay after you’ve met your deductible. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you’ll pay 20% of the cost of a medical procedure after you’ve met your deductible, and your insurance will cover the remaining 80%.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The maximum amount you’ll pay for healthcare costs in a year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance will cover 100% of your remaining healthcare expenses.
Real-World Scenarios
Imagine you have a health insurance plan with a $1,000 deductible, a $20 copay for doctor’s visits, a 20% coinsurance, and a $5,000 out-of-pocket maximum. Now, let’s see how these terms apply in real-life situations:
- Scenario 1: Doctor’s Visit You go to the doctor for a routine checkup. Your copay is $20, so you pay that amount out-of-pocket.
- Scenario 2: Emergency Room Visit You have a serious medical emergency and go to the emergency room. The bill is $5,000. Since you haven’t met your deductible yet, you pay the first $1,000. Your insurance covers the remaining $4,000, minus your 20% coinsurance ($800). Your total out-of-pocket cost for the emergency room visit is $1,800.
- Scenario 3: Major Surgery You need a major surgery that costs $10,000. You’ve already met your deductible, so your insurance covers 80% of the cost, and you pay 20% (or $2,000). However, since your out-of-pocket maximum is $5,000, you won’t pay more than that for healthcare costs throughout the year, even if your total healthcare expenses exceed $5,000.
Final Wrap-Up: What Are Good Health Insurance Companies
Finding the right health insurance is a big deal, but it doesn’t have to be a headache. By taking the time to understand your needs, compare plans, and ask questions, you can find a policy that fits your lifestyle and budget. Remember, you’re in the driver’s seat! So, get out there, explore your options, and make sure you’re protected.
Clarifying Questions
What is a deductible?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your health insurance starts covering your healthcare costs. Think of it as your personal “contribution” to the plan before insurance kicks in.
What is a copay?
A copay is a fixed amount you pay for a specific service, like a doctor’s visit or prescription. It’s like a small fee you pay for using your insurance benefits.
What is coinsurance?
Coinsurance is a percentage of the healthcare cost that you pay after you’ve met your deductible. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you’d pay 20% of the bill after you’ve reached your deductible.
How can I get a quote for health insurance?
Most health insurance companies offer online quote tools where you can enter your information and get an estimate of your premium. You can also contact an insurance agent or broker to get personalized quotes.