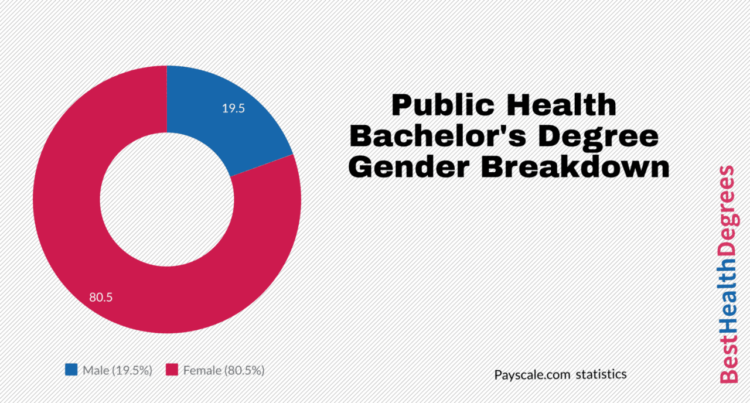
Overview of Bachelor’s in Public Health
Public Health is a broad field that focuses on the health and well-being of populations. It encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including epidemiology, biostatistics, environmental health, and health policy.
Public Health education is essential for preparing professionals to work in this field. Graduates with a Bachelor’s in Public Health are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to assess, plan, implement, and evaluate public health programs and policies.
Career Opportunities for Public Health Graduates
Public Health graduates have a wide range of career opportunities available to them. They can work in government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private companies. Some common job titles include:
- Epidemiologist
- Biostatistician
- Environmental Health Scientist
- Health Policy Analyst
- Public Health Educator
Curriculum for Bachelor’s in Public Health
The curriculum for a Bachelor’s in Public Health (BPH) program typically encompasses a diverse range of courses that provide students with a comprehensive understanding of public health principles, practices, and research methods. These courses lay the foundation for students to develop the skills and knowledge necessary to promote health, prevent disease, and improve the well-being of communities.
The core courses in a BPH program typically include:
- Introduction to Public Health: This course provides an overview of the field of public health, including its history, core concepts, and ethical considerations.
- Biostatistics: This course introduces students to the principles of biostatistics, including data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Epidemiology: This course focuses on the study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in populations.
- Environmental Health: This course examines the relationship between environmental factors and human health, and the principles of environmental health risk assessment and management.
- Health Promotion and Disease Prevention: This course emphasizes the principles and practices of health promotion and disease prevention, including behavior change strategies and community-based interventions.
- Social and Behavioral Sciences: This course explores the social and behavioral factors that influence health and well-being, and the role of social and behavioral sciences in public health practice.
The curriculum for a BPH program also emphasizes the integration of social and behavioral sciences, recognizing the significant role that social, cultural, and behavioral factors play in shaping health outcomes. Courses in sociology, psychology, and anthropology provide students with a deeper understanding of the social determinants of health and the challenges and opportunities for improving health equity.
Specializations within Bachelor’s in Public Health
Specializations within the Bachelor’s in Public Health program allow students to focus on specific areas of public health practice. These specializations provide in-depth knowledge and skills in a particular field, preparing graduates for specialized roles in the public health workforce.
Common specializations include:
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of the distribution and patterns of health-related states or events in a population. Students in this specialization learn to identify and investigate outbreaks of disease, track the spread of infections, and develop strategies to prevent and control health problems. They gain skills in data collection, analysis, and interpretation, as well as in communicating public health findings.
Graduates with a specialization in Epidemiology can pursue careers in disease surveillance, outbreak investigation, and research. They may work in government agencies, non-profit organizations, or academic institutions.
Health Education
Health Education focuses on promoting health and preventing disease through education and behavioral change. Students in this specialization learn to develop and implement health education programs, evaluate their effectiveness, and advocate for health policies. They gain skills in communication, counseling, and community outreach.
Graduates with a specialization in Health Education can pursue careers in health promotion, disease prevention, and community health. They may work in schools, community health centers, or non-profit organizations.
Environmental Health
Environmental Health focuses on the relationship between the environment and human health. Students in this specialization learn to identify and assess environmental hazards, develop strategies to reduce their impact, and promote healthy environments. They gain skills in environmental science, risk assessment, and environmental policy.
Graduates with a specialization in Environmental Health can pursue careers in environmental protection, public health policy, and sustainability. They may work in government agencies, non-profit organizations, or private industry.
Research and Practicum in Bachelor’s in Public Health
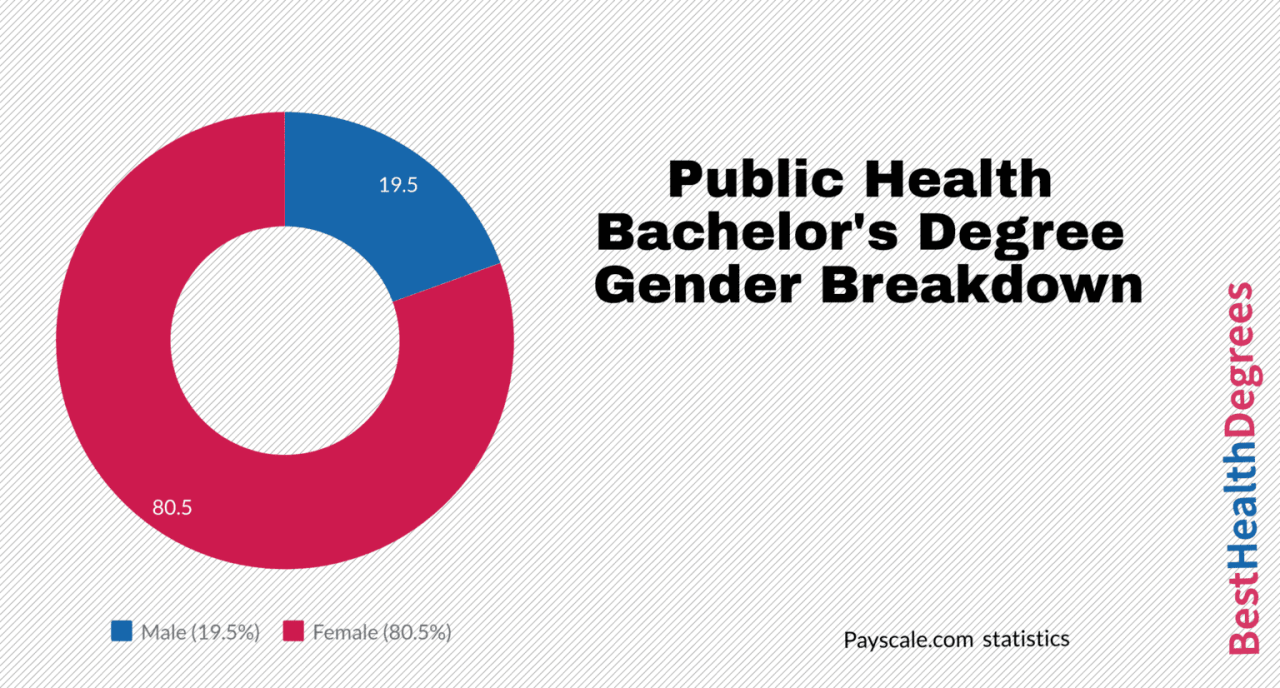
Research and practicum experiences are vital components of a Bachelor’s in Public Health program. They provide students with hands-on opportunities to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world settings.
Research projects allow students to explore public health issues in depth and contribute to the field’s body of knowledge. Practicum experiences place students in community organizations or government agencies, where they can gain practical experience in public health programming and intervention.
Types of Research Projects
Research projects in public health can cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Health disparities
- Chronic disease prevention
- Environmental health
li>Health policy
Types of Practicum Experiences
Practicum experiences in public health can take many forms, such as:
- Working with community organizations on health promotion programs
- Interning with government agencies on public health policy development
- Conducting research on public health issues
The benefits of hands-on learning for public health students are numerous. These experiences allow students to:
- Develop their research and analytical skills
- Gain practical experience in public health programming
- Build their professional network
- Prepare for careers in public health
Career Prospects for Bachelor’s in Public Health Graduates
Public Health graduates enjoy promising career prospects due to the increasing demand for professionals in the field. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 9% growth in employment for public health workers from 2021 to 2031, which is faster than the average for all occupations. The median annual salary for public health workers was $47,790 in May 2021, with the top 10% earning over $85,990.
Public Health graduates are employed in various industries and organizations, including:
Government Agencies
– Federal, state, and local health departments
– Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
– National Institutes of Health (NIH)
– World Health Organization (WHO)
Nonprofit Organizations
– American Red Cross
– United Way
– Planned Parenthood
– Habitat for Humanity
Healthcare Providers
– Hospitals
– Clinics
– Nursing homes
– Home health agencies
Education and Research Institutions
– Universities
– Colleges
– Research centers
– Public health institutes
Public Health professionals play a vital role in society by improving the health and well-being of communities. They work to prevent and control diseases, promote healthy behaviors, and ensure access to healthcare services. Their efforts have a significant impact on the quality of life for individuals and communities.