Coverage and Benefits
Commercial health insurance plans provide comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical expenses. They cover essential healthcare services such as hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs.
Coverage typically includes inpatient and outpatient care, emergency services, preventive care, and mental health services. Some plans also offer additional benefits like dental and vision coverage.
Limitations and Exclusions
While commercial health insurance plans offer extensive coverage, there are certain limitations and exclusions to be aware of. Pre-existing conditions may not be covered immediately, and certain treatments or procedures may require prior authorization.
It’s important to carefully review the policy details to understand the scope of coverage and any applicable limitations or exclusions.
Premiums and Costs
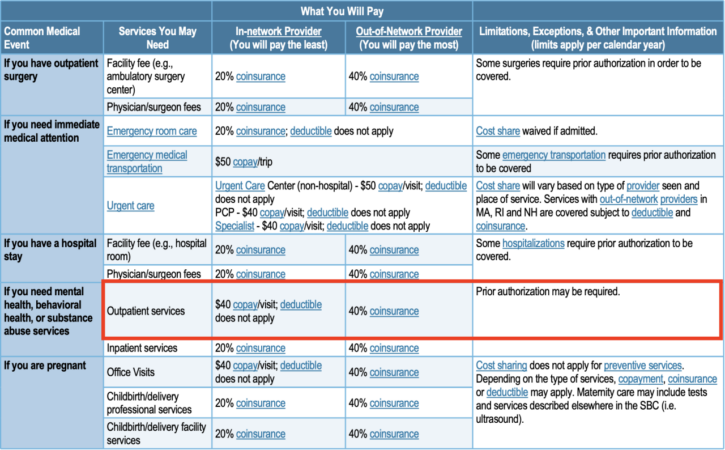
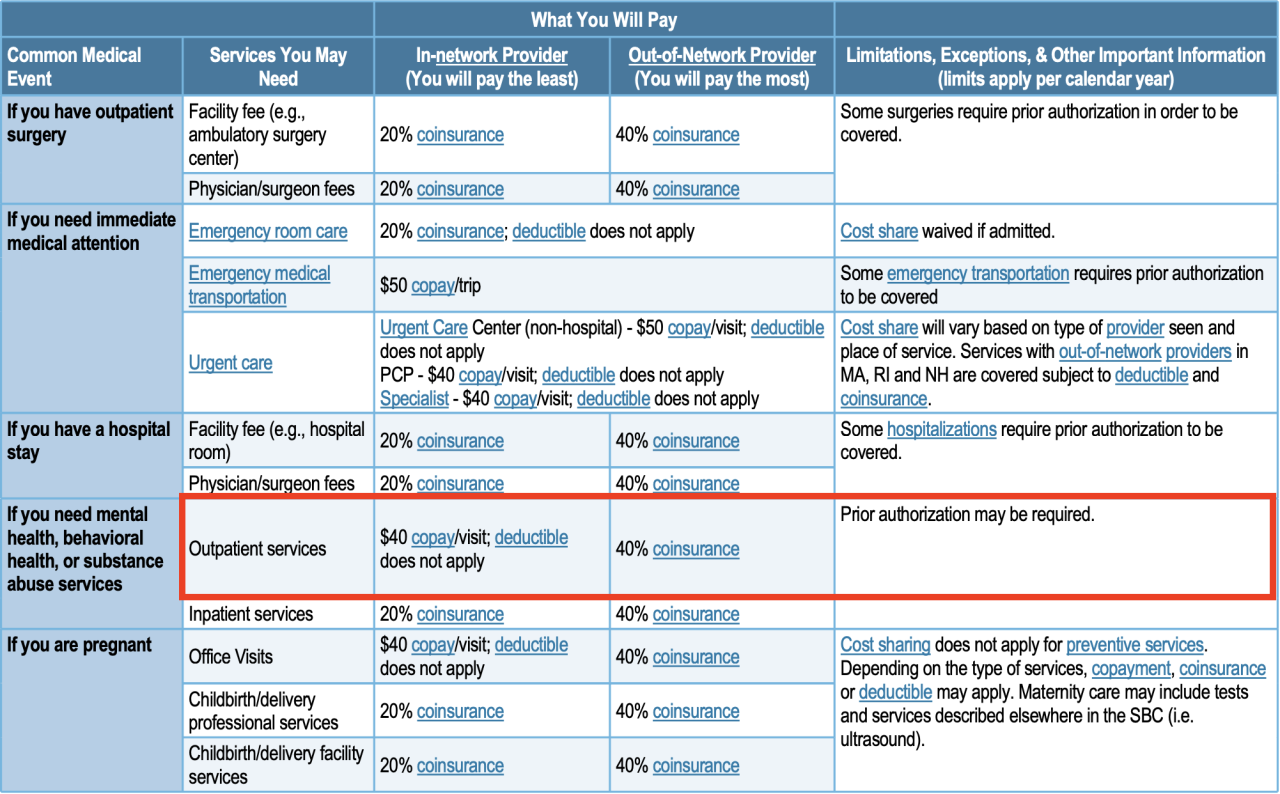
Understanding the financial aspects of commercial health insurance is crucial. Premiums, deductibles, copays, and coinsurance play significant roles in determining your out-of-pocket expenses.
Premiums are the monthly or annual payments you make to your insurance company for coverage. They are calculated based on various factors, including your age, health status, location, and the type of plan you choose. Higher-risk individuals or those with pre-existing conditions may face higher premiums.
Cost-Sharing Arrangements
Cost-sharing arrangements are designed to distribute the financial burden of healthcare expenses between you and your insurance company.
Deductible
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins. Once you meet your deductible, your insurance company starts paying a portion of your medical expenses.
Copay
A copay is a fixed amount you pay for specific healthcare services, such as doctor’s visits or prescription drugs. Copays are typically lower than the actual cost of the service.
Coinsurance
Coinsurance is a percentage of the medical expenses you pay after meeting your deductible. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you will pay 20% of the remaining medical expenses after meeting your deductible.
These cost-sharing arrangements help reduce the overall cost of health insurance premiums but can also increase your out-of-pocket expenses when you need medical care.
Plan Types and Options
Navigating the world of commercial health insurance can be daunting, but understanding the different types of plans available can help you make an informed decision. From HMOs to PPOs and EPOs, each plan offers unique advantages and considerations.
HMOs
- Advantages: Typically lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs, strong focus on preventive care.
- Disadvantages: Limited network of providers, may require referrals for specialists, less flexibility.
PPOs
- Advantages: Wider network of providers, more flexibility in choosing doctors, greater coverage for out-of-network care.
- Disadvantages: Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs, potential for higher deductibles.
EPOs
- Advantages: Similar to HMOs in terms of lower premiums and strong focus on preventive care.
- Disadvantages: Even more limited network of providers than HMOs, may not cover out-of-network care.
Ultimately, the best plan for you depends on your individual needs, preferences, and budget. Consider factors such as the size of the network, the flexibility of provider choice, and the potential costs involved.
Enrollment and Eligibility
Commercial health insurance plans typically have eligibility criteria that determine who can enroll in the plan. These criteria may include age, income, and residency requirements.
Enrollment periods vary depending on the plan and insurance provider. Open enrollment is a specific period each year when individuals can enroll in or change their health insurance plans. Special enrollment periods may also be available for individuals who experience certain life events, such as losing their job or getting married.
To apply for and enroll in a commercial health insurance plan, individuals can contact the insurance provider directly or work with an insurance agent. The application process typically involves providing personal information, such as age, income, and health history. Individuals may also need to provide proof of identity and residency.
Regulations and Compliance
The commercial health insurance industry operates within a stringent regulatory framework established by both state and federal laws. These regulations aim to protect consumers, ensure fair competition, and maintain the solvency of insurance companies.
Role of Insurance Commissioners
Insurance commissioners, appointed by each state, play a critical role in regulating the industry. They are responsible for:
- Approving insurance rates and policy forms
- Investigating complaints and enforcing compliance
- Ensuring the financial stability of insurers
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with insurance regulations is crucial for both insurers and policyholders. Insurers must adhere to regulations to avoid penalties and maintain their license to operate. Policyholders benefit from compliance as it ensures fair treatment, accurate policy information, and financial protection.