Employer-Provided Health Insurance

Employer-provided health insurance is a type of health insurance that is offered by employers to their employees. It is a common benefit in the United States, with over 156 million people covered by employer-sponsored health plans in 2021.
There are many benefits to employer-provided health insurance for both employees and employers. For employees, it can provide access to affordable health care, help them save money on their health care costs, and give them peace of mind knowing that they are covered in case of a medical emergency.
Benefits for Employers
- Improved employee morale and productivity
- Reduced absenteeism and presenteeism
- Increased employee loyalty and retention
- Enhanced company reputation as a desirable employer
Types of Employer-Provided Health Insurance Plans
Employer-provided health insurance plans vary in their structure, coverage, and costs. Understanding the different types of plans can help employees make informed decisions about their healthcare options.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs are managed care plans that provide comprehensive healthcare services through a network of contracted providers. Members must choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates their care and refers them to specialists within the network. HMOs typically have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs than other types of plans.
- Advantages:
- Lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs
- Comprehensive coverage
- Access to a network of providers
- Disadvantages:
- Limited choice of providers
- May require referrals for specialist care
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs are also managed care plans but offer more flexibility than HMOs. Members can choose any provider within the network, but they receive lower costs and benefits when using preferred providers. PPOs typically have higher premiums than HMOs but lower out-of-pocket costs.
- Advantages:
- More choice of providers
- No referrals required for specialist care
- Lower out-of-pocket costs when using preferred providers
- Disadvantages:
- Higher premiums than HMOs
- Higher out-of-pocket costs when using non-preferred providers
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs)
EPOs are similar to HMOs but offer a narrower network of providers. Members must choose a PCP within the network and receive all care from providers within the network. EPOs typically have lower premiums than PPOs but higher out-of-pocket costs.
- Advantages:
- Lower premiums than PPOs
- Comprehensive coverage
- No referrals required for specialist care
- Disadvantages:
- Narrow network of providers
- Higher out-of-pocket costs
Examples of Employer-Provided Health Insurance Plans
- Aetna:
- Offers HMO, PPO, and EPO plans
- Wide network of providers
- Competitive premiums
- Blue Cross Blue Shield:
- Offers HMO, PPO, and EPO plans
- Local networks of providers
- Focus on customer service
- UnitedHealthcare:
- Offers HMO, PPO, and EPO plans
- National network of providers
- Innovative healthcare solutions
Cost and Coverage of Employer-Provided Health Insurance
The cost of employer-provided health insurance can vary widely depending on factors such as the size of the company, the industry in which it operates, and the geographic location. Generally, larger companies tend to have lower costs due to their ability to spread the risk over a larger pool of employees. The industry in which a company operates can also affect the cost of health insurance, as some industries are more hazardous than others and require more comprehensive coverage. Geographic location can also play a role, as the cost of medical care varies from region to region.
Employer-provided health insurance plans typically offer a range of coverage options, including medical, dental, vision, and prescription drug coverage. The specific coverage provided by a plan will vary depending on the plan design and the employer’s contributions. Some plans may offer a more comprehensive level of coverage, while others may offer a more limited level of coverage.
The cost of employer-provided health insurance can be divided into two main categories: premiums and deductibles. Premiums are the monthly payments made by the employee to the insurance company. Deductibles are the amount of money that the employee must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage begins.
The cost of employer-provided health insurance can be a significant expense for both employers and employees. However, the coverage provided by these plans can help to protect employees from the financial burden of medical expenses.
Examples of Costs and Coverage
The following are some examples of the costs and coverage of employer-provided health insurance plans:
– A small company with 50 employees may pay an average of $500 per month for health insurance coverage. This coverage may include medical, dental, vision, and prescription drug coverage.
– A large company with 1,000 employees may pay an average of $300 per month for health insurance coverage. This coverage may include medical, dental, vision, and prescription drug coverage.
– A company in the healthcare industry may pay an average of $600 per month for health insurance coverage. This coverage may include medical, dental, vision, and prescription drug coverage.
– A company in the manufacturing industry may pay an average of $400 per month for health insurance coverage. This coverage may include medical, dental, and prescription drug coverage.
The cost of employer-provided health insurance can vary significantly depending on the factors discussed above. It is important to compare the costs and coverage of different plans before making a decision about which plan to choose.
Impact of Employer-Provided Health Insurance on Employee Health and Well-being
Employer-provided health insurance has a profound impact on the health and well-being of employees. Access to affordable and comprehensive healthcare through employer-sponsored plans enables individuals to seek preventive care, manage chronic conditions, and address health concerns promptly. This, in turn, leads to improved health outcomes, increased productivity, and reduced healthcare costs.
Improved Health Outcomes
Studies have consistently shown that employer-provided health insurance is associated with better health outcomes. Employees with health insurance are more likely to:
- Have regular checkups and screenings
- Manage chronic conditions effectively
- Receive timely treatment for acute illnesses and injuries
- Have lower rates of preventable diseases
For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that employees with employer-provided health insurance had a 15% lower risk of dying from heart disease and a 10% lower risk of dying from cancer compared to those without insurance.
Reduced Healthcare Costs
Employer-provided health insurance plays a crucial role in reducing healthcare costs for employees. By providing access to preventive care and early intervention, employer-sponsored plans help employees avoid costly medical expenses down the road.
Additionally, employer-provided health insurance often includes prescription drug coverage, which can significantly reduce the cost of medications for employees and their families. A study by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that employer-sponsored health insurance plans saved employees an average of $2,000 per year on prescription drug costs.
Trends and Future of Employer-Provided Health Insurance
The landscape of employer-provided health insurance is constantly evolving, driven by factors such as healthcare costs, government regulations, and employee needs. In this section, we will explore the emerging trends and discuss the potential impact of these trends on the future of employer-provided health insurance.
Emerging Trends
Some of the key trends shaping the future of employer-provided health insurance include:
- Increased Focus on Value-Based Care: Employers are increasingly seeking ways to reduce healthcare costs while improving employee health outcomes. Value-based care models, which reward providers for delivering high-quality, cost-effective care, are gaining traction.
- Adoption of Telehealth: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth services, which allow employees to access healthcare remotely. Telehealth is expected to continue to play a significant role in employer-provided health insurance, offering convenience, accessibility, and cost savings.
- Personalized Health Plans: Employers are recognizing the need for personalized health plans that meet the unique needs of their employees. This includes offering a wider range of plan options, such as high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) paired with health savings accounts (HSAs), and tailored wellness programs.
Impact of Healthcare Reform
Healthcare reform initiatives, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), have had a significant impact on employer-provided health insurance. The ACA introduced regulations aimed at expanding access to health insurance, controlling costs, and improving quality. These regulations have affected employer-provided health insurance in several ways, including:
- Expansion of Coverage: The ACA expanded health insurance coverage to millions of Americans, including many who were previously uninsured. This has led to an increase in the number of employees who are covered by employer-provided health insurance.
- Increased Costs: The ACA also introduced a number of new taxes and fees on health insurance companies, which have been passed on to employers in the form of higher premiums.
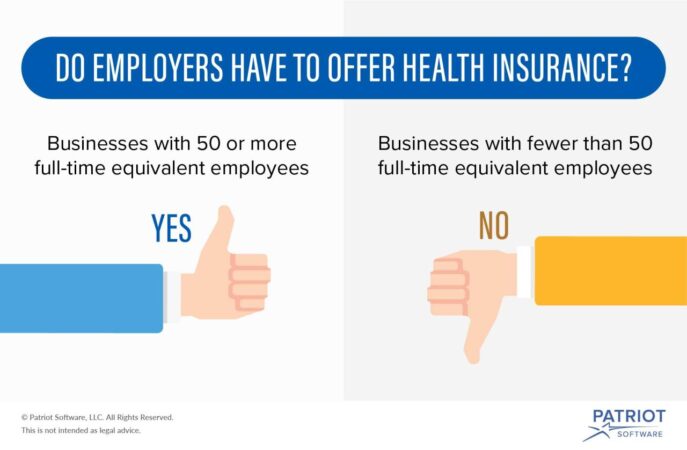
- Mandate to Provide Coverage: The ACA requires employers with 50 or more employees to offer health insurance to their employees or pay a penalty. This has led to more employers offering health insurance, but it has also increased the cost of providing health insurance for some employers.
Future of Employer-Provided Health Insurance
The future of employer-provided health insurance is uncertain, but several factors are likely to shape its evolution:
- Rising Healthcare Costs: Healthcare costs are expected to continue to rise in the future, which will put pressure on employers to find ways to control costs while still providing adequate coverage for their employees.
- Government Regulation: Government regulations will continue to play a significant role in shaping the future of employer-provided health insurance. The ACA is likely to remain in place, but future changes to the law could have a significant impact on employer-provided health insurance.
- Employee Expectations: Employees are increasingly expecting their employers to provide comprehensive and affordable health insurance. Employers who want to attract and retain top talent will need to offer competitive health insurance benefits.
In the future, employer-provided health insurance is likely to become more personalized, value-based, and technologically advanced. Employers will need to adapt to these changes in order to provide their employees with the health insurance coverage they need.