- Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums
- Risk Assessment and Underwriting
- Premium Calculation Methods
- Data and Analytics
- Types of Insurance and Premium Variations
- Premium Adjustments and Discounts
- Transparency and Consumer Understanding
- Conclusion
- Essential FAQs: How Do Insurance Companies Calculate Premiums
How do insurance companies calculate premiums? It’s a question that pops up when you’re thinking about buying a new policy, right? Like figuring out how many slices of pizza you can eat before you need a nap, it all comes down to a bunch of factors. Insurance companies use a whole system to figure out how much you should pay, and it’s not as random as you might think.
They’re basically playing a game of risk assessment, figuring out how likely you are to make a claim. Your age, location, driving history, and even your credit score can all play a part. But don’t worry, it’s not all doom and gloom. There are ways to lower your premiums, like getting good grades, keeping a clean driving record, and even making your home safer.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums
Insurance companies use a complex system to determine how much you pay for coverage, known as your premium. It’s not just about pulling a number out of a hat. They analyze various factors, aiming to balance the risk they take on by insuring you with the price they charge.
Factors Affecting Premium Calculation
Insurance companies consider various factors when determining your premium. They analyze these elements to assess the likelihood of you filing a claim, the potential cost of that claim, and ultimately, the price they need to charge you to cover their expenses and make a profit.
- Age: As you get older, the likelihood of needing health insurance increases, and your premium reflects this. Younger individuals typically have lower premiums than older ones.
- Health History: If you have pre-existing conditions or a history of health issues, your premium will likely be higher. This is because insurance companies assess the potential for costly claims.
- Lifestyle: Factors like smoking, alcohol consumption, and exercise habits influence your health and, in turn, your premium. A healthy lifestyle can result in lower premiums.
- Location: Your geographic location plays a role in your premium. Areas with higher crime rates or natural disaster risks may have higher insurance costs.
- Driving History: For auto insurance, your driving record is crucial. Accidents, speeding tickets, and DUI convictions increase your premium.
- Credit Score: Believe it or not, your credit score can impact your insurance premiums. A good credit score can often lead to lower premiums, while a poor credit score can signal higher risk.
- Vehicle Type: For auto insurance, the type of car you drive influences your premium. Luxury cars or high-performance vehicles are often more expensive to insure due to higher repair costs.
- Coverage Options: The type and amount of coverage you choose directly impact your premium. Higher coverage limits typically mean higher premiums.
Risk Assessment and Premium Calculation
Risk assessment is at the heart of insurance premium calculation. Insurance companies carefully analyze the factors mentioned above to determine the likelihood of you filing a claim and the potential cost of that claim. They use statistical models and historical data to assess risk.
“Insurance companies use sophisticated algorithms and actuarial science to calculate premiums, considering a wide range of factors that influence risk.”
This risk assessment helps them determine the price they need to charge to cover their costs, including claims, administrative expenses, and profits. The higher the risk, the higher the premium.
Risk Assessment and Underwriting

Insurance companies are in the business of managing risk. They do this by carefully assessing the likelihood of a covered event happening and the potential financial impact of that event. This process is called risk assessment, and it is a crucial part of determining insurance premiums.
Risk Assessment Process
Risk assessment is a systematic process that involves gathering information about potential risks, analyzing that information, and then evaluating the likelihood and severity of those risks. This process helps insurance companies determine the level of risk associated with each policyholder and set premiums accordingly.
Insurance companies use various methods to assess risk, including:
- Data Analysis: Insurance companies collect vast amounts of data about their policyholders, including demographics, driving history, medical records, and claims history. They use this data to identify patterns and trends that can help them predict future risk.
- Statistical Modeling: Statistical models are used to analyze data and predict the probability of future events. These models can be used to estimate the likelihood of a claim, the severity of a claim, and the cost of covering those claims.
- Underwriting Interviews: Insurance companies may conduct interviews with potential policyholders to gather more information about their risk profile. This information can be used to confirm the accuracy of the information provided on the application and to gain a better understanding of the policyholder’s individual circumstances.
- Risk Surveys: Insurance companies may use risk surveys to gather information about the potential risks associated with a particular property or activity. For example, a home insurance company might use a risk survey to assess the risk of fire, theft, or natural disasters.
Examples of Risk Evaluation
Here are some examples of how insurance companies evaluate risk:
- Auto Insurance: Insurance companies consider factors like age, driving history, location, and the type of vehicle when determining auto insurance premiums. Drivers with a history of accidents or traffic violations are considered higher risk and may have to pay higher premiums.
- Home Insurance: Insurance companies consider factors like the location of the home, the age of the home, the building materials used, and the presence of security systems when determining home insurance premiums. Homes in areas with a higher risk of natural disasters or crime may have higher premiums.
- Health Insurance: Insurance companies consider factors like age, health history, lifestyle, and family medical history when determining health insurance premiums. People with pre-existing conditions or a history of smoking may have to pay higher premiums.
Underwriting Role in Determining Premiums
Underwriting is the process of evaluating applications for insurance and determining whether to accept the risk and at what premium. Underwriters use the information gathered during the risk assessment process to make their decision.
“Underwriting is the heart of the insurance business. It is the process by which an insurance company determines whether to accept a risk, and if so, at what premium.” – Insurance Information Institute
Underwriters use a variety of factors to determine premiums, including:
- The type of coverage: Different types of insurance policies cover different risks, and the premiums will reflect the level of risk associated with each type of coverage.
- The amount of coverage: The amount of coverage you choose will affect your premium. Higher coverage amounts generally mean higher premiums.
- The deductible: Your deductible is the amount you agree to pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles generally mean lower premiums.
- The policyholder’s risk profile: Underwriters will consider the factors discussed in the risk assessment process to determine the policyholder’s individual risk profile.
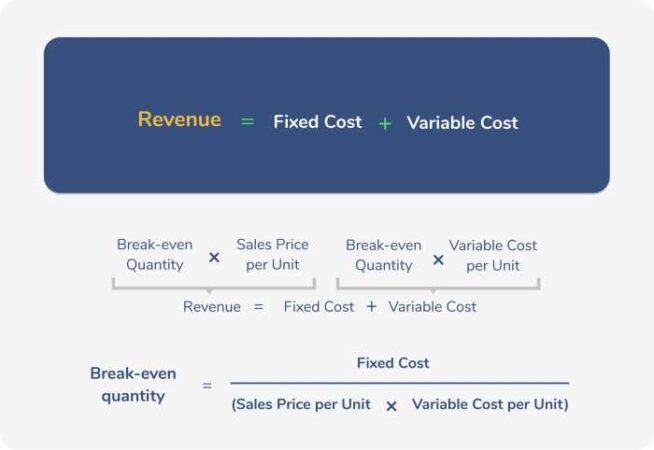
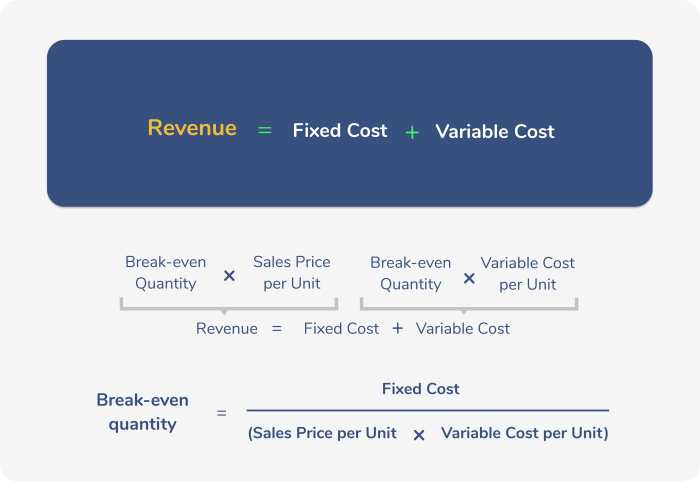
Premium Calculation Methods

Insurance companies use various methods to calculate premiums, which are the amounts policyholders pay for coverage. These methods aim to ensure that premiums are fair and reflect the risk associated with each policy. The process involves assessing risk factors, determining the likelihood of claims, and calculating the expected cost of coverage.
Actuarial Methods
Actuarial methods are the most common and rigorous approach to calculating premiums. These methods involve using historical data, statistical models, and expert judgment to predict future claims and determine the cost of coverage.
- Probability-Based Methods: These methods use probability theory to estimate the likelihood of claims occurring based on historical data and statistical models. This involves analyzing past claims data to identify patterns and trends, and using these patterns to project future claims.
- Loss Ratio Method: This method focuses on the relationship between premiums collected and claims paid. It involves calculating the loss ratio, which is the ratio of claims paid to premiums earned. The loss ratio helps insurers determine the adequacy of premiums and adjust them accordingly.
- Credibility Theory: This method accounts for the uncertainty associated with limited historical data, especially for new or niche insurance products. It combines historical data with expert judgment and statistical techniques to estimate future claims. This method helps insurers make informed decisions about premiums even when limited data is available.
Ratemaking
Ratemaking is the process of setting premiums for different groups of policyholders based on their risk profiles. This involves classifying policyholders into different risk categories and assigning premiums accordingly.
- Risk Classification: This involves grouping policyholders into categories based on shared characteristics that influence their risk of experiencing a claim. These characteristics can include age, gender, driving history, health status, location, and other relevant factors.
- Rate Development: Once policyholders are classified, insurers develop rates for each risk category. This involves determining the cost of coverage for each category, considering factors such as claims history, risk assessment, and operational expenses.
- Rate Adjustment: Insurers periodically review and adjust rates to reflect changes in risk profiles, claims experience, and market conditions. These adjustments ensure that premiums remain fair and competitive.
Other Methods
In addition to actuarial methods and ratemaking, insurers may use other methods to calculate premiums, such as:
- Experience Rating: This method uses the policyholder’s own claims history to adjust premiums. Policyholders with a lower claims history may receive lower premiums, while those with a higher claims history may face higher premiums.
- Manual Rating: This method involves using a predetermined set of rates based on specific factors, such as the type of coverage, the value of the insured asset, and the location. This method is typically used for simpler insurance products with limited risk variations.
Data and Analytics
Insurance companies are like detectives, constantly gathering clues to understand their customers’ risk profiles. They use data and analytics to build a clearer picture of who’s likely to file a claim and how much it might cost. This helps them set premiums that are fair for both the customer and the company.
Data Sources Used for Premium Modeling
Insurance companies use a wide range of data sources to refine their premium calculations. These sources provide valuable insights into risk factors and help them develop more accurate pricing models.
Here are some examples:
- Demographic Data: This includes factors like age, gender, location, occupation, and marital status. For example, a young driver with a high-performance car might pay more than an older driver with a family sedan.
- Driving Records: This data includes information about past accidents, traffic violations, and driving history. A driver with a clean record might receive a lower premium than someone with multiple speeding tickets.
- Credit History: Believe it or not, your credit score can impact your insurance premiums! This is because it’s considered a measure of your financial responsibility, which can be linked to your likelihood of paying your premiums on time.
- Vehicle Data: The make, model, year, and safety features of your car play a big role in your insurance premium. A newer car with advanced safety features will generally cost less to insure than an older car with fewer safety features.
- Claims History: This data tracks previous claims made by individuals and provides valuable insights into their risk profiles. People with a history of frequent claims might face higher premiums.
- External Data Sources: Insurance companies also leverage external data sources, like weather data, traffic patterns, and even crime statistics, to understand potential risks in different geographic areas.
Impact of Technology and Artificial Intelligence on Premium Calculation
Technology and artificial intelligence (AI) are changing the game for insurance companies. These advancements are enabling them to analyze data faster, identify patterns more effectively, and develop more sophisticated pricing models.
“AI-powered algorithms can process vast amounts of data, identify hidden correlations, and predict future outcomes with greater accuracy than traditional methods.”
Here are some ways technology is impacting premium calculations:
- Automated Risk Assessment: AI algorithms can automate the risk assessment process, analyzing data from various sources to quickly assess an individual’s risk profile.
- Personalized Pricing: AI allows for more personalized pricing by considering individual factors and providing customized premiums based on specific risk profiles.
- Fraud Detection: AI can help detect fraudulent claims by identifying patterns and anomalies in data, reducing insurance fraud and keeping premiums lower for everyone.
- Predictive Modeling: AI-powered models can predict future claims with greater accuracy, allowing insurance companies to adjust premiums proactively and manage risk more effectively.
Types of Insurance and Premium Variations
Insurance premiums are the lifeblood of the insurance industry, and understanding how they’re calculated is crucial for both consumers and insurers. While the basic principles of risk assessment and underwriting are common across different types of insurance, there are significant variations in how premiums are determined for specific policies. This section dives into the diverse world of insurance premiums, exploring the unique characteristics of different types of insurance and how they influence premium calculations.
Premium Calculation Methods for Different Insurance Types
Premium calculation methods vary widely depending on the type of insurance. Here’s a table comparing the common methods used for life, health, and auto insurance:
| Insurance Type | Premium Calculation Method | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Life Insurance |
|
|
| Health Insurance |
|
|
| Auto Insurance |
|
|
Key Factors Influencing Premium Variations
Each type of insurance has its own set of factors that significantly influence premium variations. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common factors:
Life Insurance
- Age: As individuals get older, their mortality risk increases, leading to higher premiums. This is a major factor, and you’ll see a noticeable difference in premiums between a 25-year-old and a 55-year-old.
- Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions or risky lifestyles (smoking, excessive alcohol consumption) may face higher premiums. Insurance companies assess these factors to gauge the likelihood of early death and adjust premiums accordingly.
- Death Benefit Amount: The higher the death benefit, the higher the premium. It’s a simple correlation: a larger payout means a higher cost for the insurance company. Think of it like a bigger “bet” on your life.
- Policy Term: The length of the policy term also affects premiums. Longer terms generally lead to higher premiums because the insurer assumes a longer risk.
Health Insurance
- Age: Similar to life insurance, older individuals tend to have higher health insurance premiums. As people age, they’re more likely to experience health issues, leading to higher healthcare costs.
- Health History: Pre-existing conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or cancer can result in higher premiums. Insurance companies consider your past medical history to estimate your future healthcare needs and associated costs.
- Location: The cost of healthcare varies across different regions. Areas with higher healthcare costs tend to have higher health insurance premiums.
- Coverage Plan: Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage. More comprehensive plans with lower deductibles and co-pays generally have higher premiums. It’s a trade-off between the level of coverage and the cost.
Auto Insurance
- Vehicle Value: More expensive vehicles typically have higher premiums because the cost of repair or replacement is greater. Think about it – a luxury sports car is going to be more expensive to fix than a basic sedan.
- Driving Record: Your driving history is a major factor in auto insurance premiums. Accidents, speeding tickets, and other violations increase your risk of future claims, resulting in higher premiums. Keep that driving record clean!
- Location: Urban areas with high traffic density and more accidents generally have higher auto insurance premiums. Insurance companies consider the risk of accidents in different locations.
- Usage: How often you drive your car affects your premium. Those who drive frequently or for long distances are more likely to be involved in accidents, leading to higher premiums.
Specific Insurance Policies and Premium Calculations
- Life Insurance:
- Term Life Insurance: Provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. Premiums are generally lower than permanent life insurance because the coverage is temporary.
- Whole Life Insurance: Offers lifetime coverage with a cash value component. Premiums are typically higher than term life insurance due to the permanent coverage and the cash value feature.
- Universal Life Insurance: Provides flexible premiums and death benefit options. Premiums can fluctuate based on market interest rates and the policyholder’s choices.
- Health Insurance:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): Requires you to choose a primary care physician within the network. Premiums are typically lower than other plans, but you have limited out-of-network coverage.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): Offers more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. Premiums are generally higher than HMOs, but you have more out-of-network options.
- High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): Has a high deductible but lower premiums. It’s often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA) to help cover healthcare expenses.
- Auto Insurance:
- Liability Coverage: Covers damage to other vehicles or property and injuries to other people in an accident. This is typically required by law.
- Collision Coverage: Covers damage to your own vehicle in an accident, regardless of fault. This is optional and can be expensive.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Covers damage to your vehicle from events other than accidents, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. This is also optional.
Premium Adjustments and Discounts
Insurance companies strive to make their pricing fair and reflective of individual risks. While they use complex calculations to determine initial premiums, they also offer adjustments and discounts to acknowledge individual circumstances and encourage positive behavior. These adjustments can significantly impact the final premium you pay, so understanding how they work is essential.
Premium Adjustments
Premium adjustments are changes to your insurance premium based on factors that can affect your risk profile. These adjustments can be positive (lowering your premium) or negative (increasing your premium).
- Claims History: A clean driving record or no recent home insurance claims will generally result in lower premiums. Conversely, a history of accidents or claims will likely lead to higher premiums. Insurance companies consider this a strong indicator of future risk.
- Safety Measures: Installing safety features in your home, like smoke detectors and security systems, can lower your homeowner’s insurance premium. Similarly, using safety equipment while driving, like anti-theft devices or driver assistance features, can reduce your car insurance premium.
- Policy Changes: Changes to your insurance policy, like increasing your deductible or lowering your coverage, can affect your premium. A higher deductible usually means a lower premium, as you agree to pay more out-of-pocket in case of a claim. Conversely, adding coverage, such as comprehensive or collision insurance, can increase your premium.
Discounts
Insurance companies offer a variety of discounts to reward policyholders who take steps to reduce their risk or demonstrate responsible behavior.
- Good Student Discount: Students with good grades often receive discounts on car insurance, as they are statistically less likely to be involved in accidents. This discount can be a significant incentive for students to maintain good academic performance.
- Safe Driver Discount: Drivers with a clean driving record for a specified period (usually several years) may qualify for a safe driver discount. This reflects the lower risk associated with drivers who have consistently demonstrated safe driving practices.
- Multi-Policy Discount: Bundling multiple insurance policies, such as car and home insurance, with the same company often leads to a discount. This is because insurance companies can streamline their operations and reduce costs by managing multiple policies for the same customer.
- Loyalty Discount: Some insurance companies offer loyalty discounts to long-term customers who have maintained their policies without any significant issues. This is a way for insurance companies to reward customer loyalty and encourage continued business.
Impact of Adjustments and Discounts, How do insurance companies calculate premiums
Premium adjustments and discounts directly impact the final premium you pay. Positive adjustments and discounts lower your premium, while negative adjustments increase it. The specific impact of each adjustment or discount will depend on the individual policy and the specific circumstances.
It’s important to note that the availability and value of adjustments and discounts can vary significantly between insurance companies. It’s always advisable to compare quotes from multiple insurers to ensure you are getting the best possible rate.
Transparency and Consumer Understanding
Insurance premiums are the price you pay for the peace of mind that comes with knowing you’re protected in case of unexpected events. But figuring out how these premiums are calculated can feel like deciphering a secret code. The good news is, understanding the factors that influence your premium can help you make informed decisions about your insurance coverage.
Key Information for Consumers
It’s crucial for insurance companies to be transparent about their premium calculation process. This means providing consumers with clear and concise information about how their premiums are determined. Here’s a table outlining the key information that insurance companies should provide to consumers:
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Coverage Details | A breakdown of the specific types of coverage included in the policy, along with their limits and deductibles. |
| Risk Factors | An explanation of the factors that influence the premium, such as age, driving history, credit score, and location. |
| Pricing Model | A description of the methods used to calculate premiums, including any algorithms or formulas employed. |
| Premium Breakdown | A detailed breakdown of the premium components, such as coverage costs, administrative fees, and profit margins. |
| Discount Opportunities | Information about available discounts, such as safe driving discounts, bundling discounts, or good student discounts. |
| Premium Adjustment Process | An explanation of how premiums are adjusted based on changes in risk factors, such as an improvement in driving history or a change in location. |
Tips for Understanding Your Insurance Premiums
Here are some tips to help you better understand your insurance premiums:
- Read your policy carefully: Take the time to understand the terms and conditions of your policy, including the coverage details, deductibles, and exclusions. This will help you understand what you’re paying for.
- Ask questions: Don’t hesitate to ask your insurance agent or company representatives for clarification on anything you don’t understand. They are there to help you.
- Compare quotes: Get quotes from multiple insurance companies to compare prices and coverage options. This can help you find the best value for your needs.
- Shop around regularly: Don’t assume your current policy is still the best option. Review your insurance needs periodically and compare quotes from different providers to ensure you’re getting the best deal.
- Consider discounts: Many insurance companies offer discounts for good driving records, bundling policies, and other factors. Ask about available discounts and see if you qualify.
Importance of Transparency and Clear Communication
Transparency and clear communication are essential in the insurance industry. When consumers understand how their premiums are calculated, they can make informed decisions about their coverage and feel confident in their choices. This also builds trust between consumers and insurance companies, fostering a more positive and collaborative relationship. In an industry where trust is paramount, clear communication and transparency are key ingredients for building a strong and lasting relationship with your customers.
Conclusion
So, the next time you’re wondering how insurance companies decide on your premium, remember that it’s a complex but fascinating process. They’re not just pulling numbers out of thin air. They’re taking a calculated risk, based on your unique circumstances. And the more you understand how it works, the better equipped you’ll be to find the best coverage at the right price.
Essential FAQs: How Do Insurance Companies Calculate Premiums
What’s the difference between a deductible and a premium?
Your premium is the monthly payment you make for your insurance policy. Your deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in to cover the rest.
How often do insurance premiums change?
Premiums can change periodically, sometimes annually, based on factors like your claims history, changes in your risk profile, and market conditions.
Can I negotiate my insurance premium?
You can always try! Insurance companies are open to negotiation, especially if you have a good track record. Be prepared to discuss your risk profile and ask about discounts.