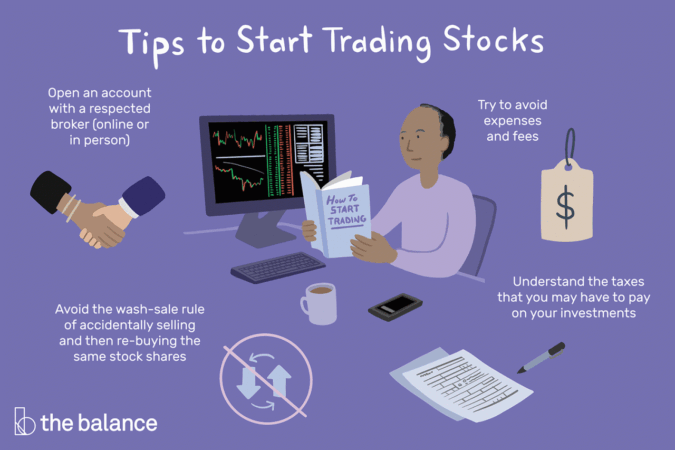
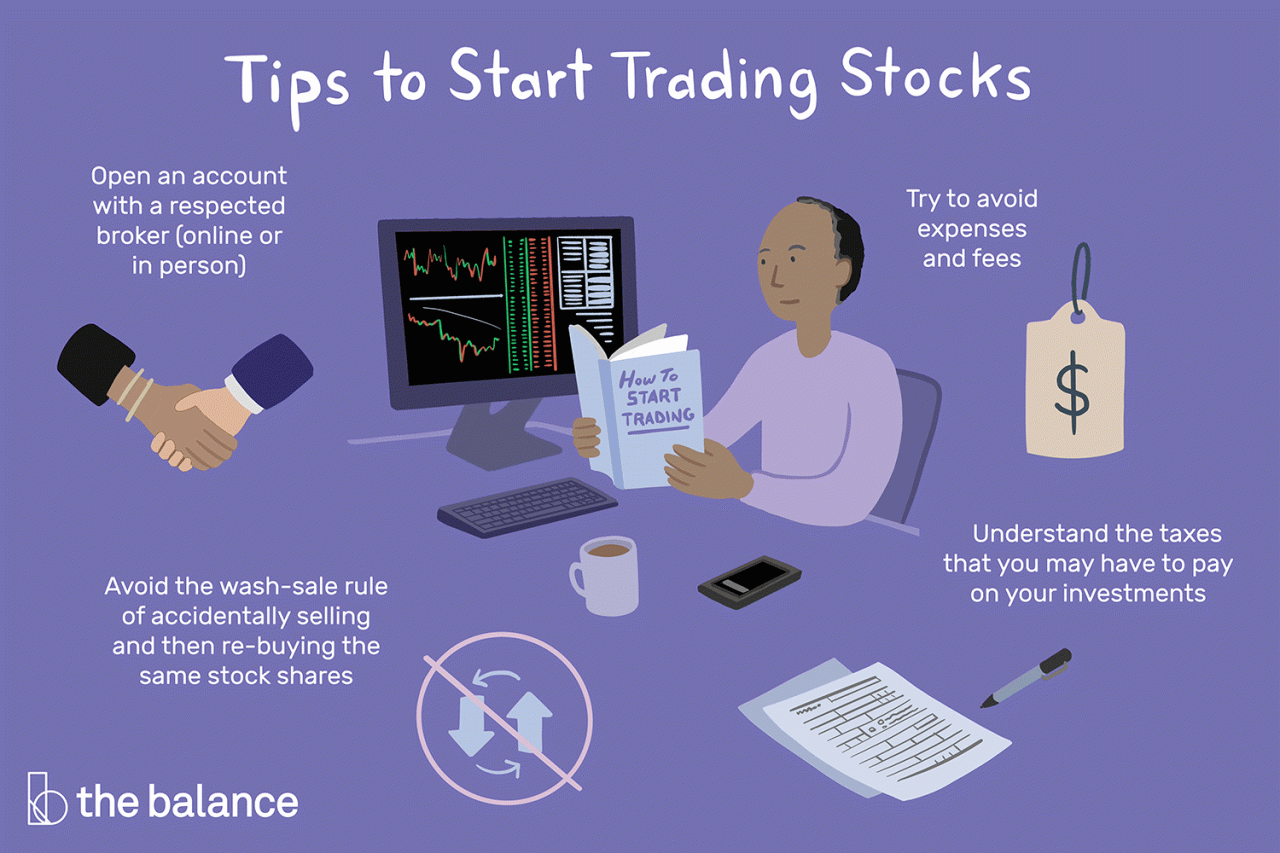
How to start trading stocks is a question many people ask, especially in today’s digital age where investing feels more accessible than ever. The stock market, a complex system of buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies, can seem daunting, but it’s actually a great way to potentially grow your wealth over time. Whether you’re a college student looking to learn about finances or a seasoned professional seeking to diversify your portfolio, understanding the basics of stock trading can open doors to exciting opportunities.
This guide will break down the process of getting started, from choosing a brokerage account to placing your first trade. We’ll explore the different types of stocks, how to research and analyze potential investments, and the importance of managing your portfolio effectively.
Choosing Stocks to Trade: How To Start Trading Stocks
Picking the right stocks is crucial for successful trading. Think of it like choosing the right ingredients for a delicious meal – you need to carefully consider what you’re looking for and how it will fit into your overall strategy. We’ll explore some key factors to consider and dive into different methods for researching and analyzing stocks.
Understanding Your Investment Goals
It’s essential to define your investment goals before diving into stock selection. What are you hoping to achieve? Are you looking for long-term growth, short-term profits, or a balance of both? Understanding your goals helps you narrow down your search and choose stocks that align with your risk tolerance and investment timeline. For example, if you’re seeking long-term growth, you might focus on companies with strong fundamentals and a history of consistent earnings. On the other hand, if you’re aiming for short-term profits, you might consider stocks with high volatility and potential for quick gains.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis delves into a company’s financial health and future prospects. It’s like reading a company’s financial report card to understand its strengths, weaknesses, and potential for growth. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Revenue and Profitability: Analyze a company’s revenue growth, profitability margins, and earnings per share (EPS) to assess its financial performance.
- Debt Levels: High debt levels can indicate financial risk. Look for companies with manageable debt loads and strong cash flow.
- Management Quality: A strong management team can significantly impact a company’s success. Research the experience and track record of the company’s leadership.
- Industry Outlook: Consider the overall health and growth potential of the industry in which the company operates. Is the industry experiencing growth or decline? Are there any upcoming trends or regulations that could impact the company’s future?
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis focuses on historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends that can predict future price movements. It’s like reading the tea leaves of the stock market. Here are some key techniques:
- Moving Averages: These are calculated by averaging a stock’s price over a specific period. Moving averages can help identify trends and potential support or resistance levels.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. An RSI above 70 indicates a stock may be overbought, while an RSI below 30 suggests it may be oversold.
- Chart Patterns: Technical analysts often look for recurring chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles, which can provide insights into potential price movements.
Identifying Potential Investment Opportunities
Once you’ve mastered fundamental and technical analysis, you can start to identify potential investment opportunities. Here are some strategies:
- Screen for Stocks: Use online stock screeners to filter stocks based on specific criteria, such as industry, market capitalization, price-to-earnings ratio (P/E), and dividend yield.
- Follow Market News and Trends: Stay informed about industry news, economic data, and market trends to identify potential investment opportunities. For example, a new technology breakthrough or a favorable economic report could trigger a stock price surge.
- Look for Value Stocks: Value stocks are companies that are trading below their intrinsic value. This could be due to temporary market conditions or investor sentiment. Identifying undervalued stocks can potentially offer significant returns.
- Consider Growth Stocks: Growth stocks are companies with high growth potential, often in emerging industries or with innovative products or services. These stocks can offer significant returns but also carry higher risk.
Important Considerations
Remember that stock trading involves risk. Always conduct thorough research and understand the risks associated with any investment before making a decision. Diversify your portfolio to reduce risk and consider seeking professional advice if needed.
Placing Your First Trade
Now that you’ve chosen your stock, it’s time to take the plunge and place your first trade! But before you hit that “buy” button, there are a few things you need to know about the different types of orders and how they work.
Types of Stock Orders
Understanding the different types of stock orders is crucial for executing your trades effectively and managing your risk.
- Market Order: This is the most common type of order, where you buy or sell a stock at the current market price. Market orders are executed immediately, ensuring you get your trade filled quickly, but you may not get the exact price you wanted.
- Limit Order: This allows you to set a specific price you’re willing to buy or sell a stock. If the market price reaches your limit price, your order will be executed. This gives you more control over the price you pay, but it doesn’t guarantee your order will be filled. For example, if you set a limit order to buy a stock at $50, but the price never drops to that level, your order won’t be filled.
- Stop-Loss Order: This order is designed to limit your potential losses on a stock. You set a specific price below your entry price (for a long position) or above your entry price (for a short position). If the stock price reaches your stop-loss price, your order will be triggered, and your position will be closed. Stop-loss orders are helpful for managing risk and protecting your portfolio from significant losses. However, they can also be triggered by market volatility, resulting in a loss even if the stock eventually recovers.
- Take-Profit Order: This order is used to lock in profits on a stock. You set a specific price above your entry price (for a long position) or below your entry price (for a short position). If the stock price reaches your take-profit price, your order will be triggered, and your position will be closed. Take-profit orders can help you secure profits and avoid holding a stock for too long, which can expose you to potential losses.
Placing a Trade
The process of placing a trade is usually straightforward. You’ll need to select the stock you want to trade, choose your order type (market, limit, stop-loss, or take-profit), enter the quantity of shares you want to buy or sell, and confirm your order.
For example, if you wanted to buy 100 shares of Apple (AAPL) at a market price, you would select AAPL as the stock, choose “market order” as the order type, enter 100 as the quantity, and click “buy.” Your order would be executed immediately at the current market price.
Managing Your Position
Once you’ve placed a trade, it’s important to monitor your position and make adjustments as needed. This includes:
- Checking the price of the stock: You should regularly check the price of the stock you’ve bought or sold to see how it’s performing. You can use a stock charting platform or your brokerage account to track the price.
- Adjusting your stop-loss or take-profit orders: As the price of the stock changes, you may need to adjust your stop-loss or take-profit orders to reflect your current risk tolerance and investment strategy. For example, if you bought a stock at $50 and set a stop-loss at $45, but the price drops to $47, you might want to adjust your stop-loss to $46 to give yourself more room for the stock to recover.
- Considering exiting your position: If the stock is performing poorly or you’re no longer comfortable holding it, you may want to consider selling your shares. This could be due to a change in your investment strategy, a decline in the company’s fundamentals, or simply a change in your risk tolerance.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are valuable tools for managing risk and securing profits. However, it’s important to set them strategically.
- Setting a stop-loss: A good rule of thumb is to set your stop-loss order at a level that represents your maximum acceptable loss. For example, if you’re comfortable losing 10% of your investment, you would set your stop-loss order 10% below your entry price.
- Setting a take-profit: Your take-profit order should be set at a level that represents your desired profit. For example, if you’re hoping to make a 20% profit, you would set your take-profit order 20% above your entry price. It’s important to remember that setting a take-profit order doesn’t guarantee you’ll make a profit. The stock price may never reach your take-profit level, or it may fall below your entry price before you can sell.
Managing Your Portfolio

Once you’ve placed your first trade and started building your portfolio, it’s crucial to manage it effectively. This involves actively monitoring your investments, making adjustments as needed, and developing strategies to protect your capital and maximize potential returns.
Diversifying Your Investments
Diversification is a fundamental principle of investing, and it’s essential for managing risk. It involves spreading your money across various asset classes, sectors, and individual stocks to reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio.
- Asset Classes: Diversifying across different asset classes like stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities can help mitigate risk. Stocks are considered growth assets, while bonds provide stability and income. Real estate offers potential for appreciation and rental income, and commodities like gold can act as a hedge against inflation.
- Sectors: Within the stock market, diversifying across different sectors like technology, healthcare, energy, and consumer goods can help you benefit from the growth of various industries.
- Individual Stocks: Investing in a variety of individual stocks within different sectors can further diversify your portfolio. This helps reduce the risk associated with any single company’s performance.
Risk Management
Risk management is crucial for protecting your capital and ensuring your portfolio’s long-term success. It involves understanding the potential risks associated with your investments and developing strategies to mitigate them.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders are pre-programmed instructions that automatically sell your shares if they fall below a specific price. This can help limit your losses if a stock’s price declines significantly.
- Control Position Size: The amount of money you invest in any single stock should be a percentage of your overall portfolio, not your entire capital. This helps prevent substantial losses if a stock performs poorly.
- Diversify Your Investments: Diversification is a fundamental risk management strategy. By spreading your investments across various asset classes, sectors, and individual stocks, you can reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio.
Controlling Trading Emotions, How to start trading stocks
Emotions can significantly impact investment decisions, leading to impulsive actions and poor outcomes. It’s crucial to control your trading emotions and make rational decisions based on sound analysis and a well-defined investment strategy.
- Avoid Fear and Greed: Fear can lead to selling stocks prematurely during market downturns, while greed can cause you to hold onto losing investments for too long. It’s important to stay disciplined and follow your investment plan.
- Don’t Chase Returns: Trying to time the market or chase high returns can lead to impulsive decisions and potentially significant losses. Focus on long-term growth and stick to your investment strategy.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you find it challenging to control your emotions or manage your portfolio effectively, consider seeking professional financial advice from a qualified advisor.
Monitoring Your Portfolio
Regularly monitoring your portfolio is crucial for staying informed about its performance and identifying potential adjustments needed to maintain your investment goals.
- Review Your Investments Regularly: It’s a good practice to review your portfolio at least quarterly to assess its performance and make any necessary adjustments.
- Track Your Performance: Keep track of your portfolio’s performance over time to identify trends and areas for improvement. This can help you refine your investment strategy and make informed decisions.
- Adjust Your Strategy: As your investment goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions change, you may need to adjust your investment strategy. For example, you might rebalance your portfolio to allocate more or less to specific asset classes or sectors.
Learning from Experience

The stock market is a dynamic and unpredictable environment. Even experienced traders make mistakes. The key to success is to learn from those mistakes and continuously improve your trading strategy.
Tracking Your Performance
Tracking your trading performance is crucial for understanding your strengths and weaknesses. You can use a spreadsheet or a trading journal to record your trades, including the entry and exit points, the profit or loss, and the reasoning behind your decisions. This data can help you identify patterns in your trading behavior and areas where you can improve.
Learning from Mistakes
Every mistake is an opportunity to learn. When you experience a loss, analyze the trade to understand why it went wrong. Did you make a poor entry or exit decision? Did you fail to manage your risk properly? By identifying the root cause of your mistakes, you can avoid repeating them in the future.
Resources for Continuing Education
There are many resources available to help you stay informed about the stock market and improve your trading skills. Some popular resources include:
- Online Trading Platforms: Most online trading platforms offer educational resources, such as articles, videos, and webinars, to help you learn about the stock market and trading strategies.
- Financial News Websites: Websites like Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, and MarketWatch provide real-time stock quotes, market analysis, and news articles that can help you stay informed about market trends.
- Books and Courses: There are many books and courses available that can teach you about the stock market and trading strategies. Look for resources from reputable authors and institutions.
Importance of Patience and Discipline
Patience and discipline are essential for successful trading. The stock market is not a get-rich-quick scheme. It takes time, effort, and discipline to develop a successful trading strategy.
“The market can stay irrational longer than you can stay solvent.” – John Maynard Keynes
This quote emphasizes the importance of patience and discipline in trading. It’s easy to get caught up in the excitement of the market and make impulsive decisions. However, it’s important to stick to your trading plan and avoid letting emotions influence your decisions.
Last Word
Remember, investing in the stock market carries inherent risks, but with careful research, a well-thought-out strategy, and a healthy dose of patience, you can navigate this exciting world of financial growth. As you gain experience, you’ll develop your own trading style and learn to manage your portfolio effectively. The journey of becoming a savvy investor is ongoing, so keep learning, adapt to changing market conditions, and never stop seeking new knowledge. So, dive in, explore the world of stock trading, and start building your financial future!
FAQ
What is the minimum amount I need to start trading stocks?
There’s no set minimum amount, but most brokerages have different requirements. Some allow you to start with just a few hundred dollars, while others may require a higher initial deposit.
How do I choose a good brokerage account?
Consider factors like trading fees, research tools, customer support, and the types of accounts they offer. Research and compare different brokerages to find one that suits your needs.
What are some popular stock trading apps?
Robinhood, Webull, TD Ameritrade, and Fidelity are just a few popular options, each offering different features and benefits. Explore these and others to see what aligns with your trading style.
Is it better to invest in individual stocks or ETFs?
It depends on your risk tolerance and investment goals. ETFs (exchange-traded funds) provide diversification, while individual stocks offer higher potential returns but also carry more risk.