
- Understanding Power of Attorney in the Context of KAR US
- Creating and Executing a Power of Attorney in KAR US
- Responsibilities and Powers of the Attorney-in-Fact
- Terminating a Power of Attorney in KAR US
- Real-World Applications of Power of Attorney in KAR US: Kar Us Power Of Attorney
- Summary
- Question & Answer Hub
KAR US Power of Attorney delves into the intricate world of legal representation, exploring the crucial role it plays in safeguarding individuals’ rights and interests. Power of Attorney (POA) empowers individuals to appoint a trusted person, known as an attorney-in-fact, to make decisions on their behalf when they are unable or unwilling to do so themselves.
This comprehensive guide examines the legal framework, types, creation, execution, responsibilities, termination, and real-world applications of POA within the KAR US context. By understanding the nuances of POA, individuals can navigate complex situations with confidence and ensure their wishes are respected.
Understanding Power of Attorney in the Context of KAR US
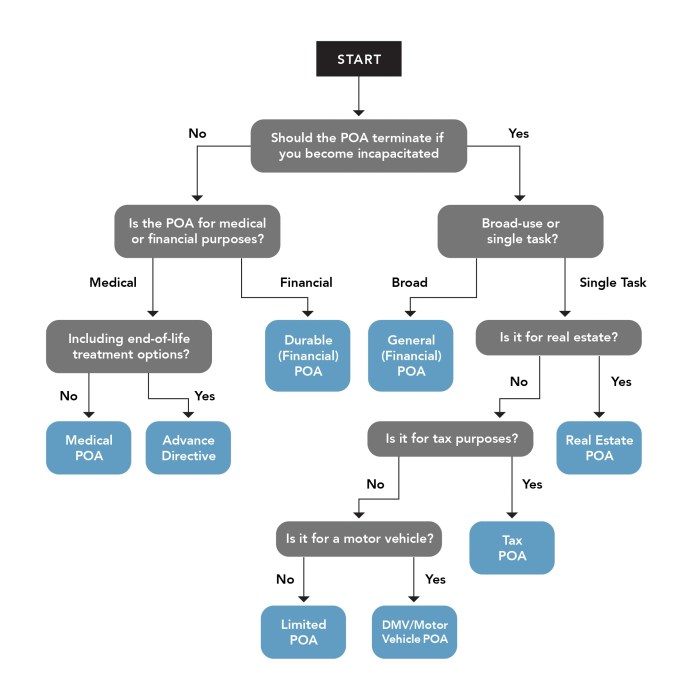
A Power of Attorney (POA) is a legal document that grants an individual, known as the “agent,” the authority to act on behalf of another person, the “principal,” in specific or general matters. This document is essential for individuals who may be unable to handle their affairs due to illness, travel, or other reasons.
In the context of KAR US, a Power of Attorney plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of a business, especially when the owner or a key decision-maker is unavailable. It empowers a designated agent to make important decisions, manage assets, and handle legal and financial matters on the principal’s behalf.
Types of Power of Attorney Relevant to KAR US
A Power of Attorney can be categorized into different types, each with specific powers and limitations. The most common types relevant to KAR US are:
- General Power of Attorney: This grants the agent broad authority to act on the principal’s behalf in most situations, including managing finances, real estate transactions, and legal matters. However, it usually does not cover healthcare decisions.
- Durable Power of Attorney: This type of POA remains effective even if the principal becomes incapacitated. It is essential for individuals who want to ensure their affairs are managed even if they are unable to make decisions for themselves.
- Healthcare Power of Attorney: This document specifically authorizes an agent to make healthcare decisions for the principal if they are unable to do so themselves. It is crucial for individuals who want to ensure their wishes are respected in medical emergencies or long-term care situations.
Examples of Situations Where POA is Crucial in KAR US
Power of Attorney is vital in various situations in the KAR US context. Some common examples include:
- Business Ownership: If the owner of a KAR US business is traveling or unable to manage daily operations, a POA can empower a trusted individual to handle critical business decisions, such as signing contracts, managing finances, and representing the business in legal matters.
- Real Estate Transactions: In case of a real estate transaction, a POA can authorize an agent to sign documents, negotiate with buyers or sellers, and handle all aspects of the transaction on the principal’s behalf.
- Medical Emergencies: If a KAR US resident is involved in an accident or falls ill, a healthcare POA can ensure their medical wishes are respected and that their designated agent can make important decisions about their care.
- Financial Management: When a KAR US resident is incapacitated or unable to manage their finances, a durable POA can allow a trusted agent to access their bank accounts, pay bills, and manage their investments.
Creating and Executing a Power of Attorney in KAR US
A Power of Attorney (POA) in KAR US is a legal document that grants an individual, known as the “agent,” the authority to act on behalf of another person, the “principal,” in specific or general matters. This document empowers the agent to make decisions and take actions on the principal’s behalf, often during situations where the principal is unable to act for themselves.
Steps Involved in Creating and Executing a Valid POA in KAR US
Creating and executing a valid POA in KAR US involves several crucial steps. These steps ensure that the document is legally sound and enforceable, safeguarding the interests of both the principal and the agent.
- Identify the Principal and Agent: Clearly identify the principal, the person granting the power, and the agent, the person receiving the authority. Both individuals must be legally competent and capable of understanding the terms of the POA.
- Define the Scope of Authority: The POA should explicitly Artikel the agent’s powers and limitations. This includes specifying the types of transactions, decisions, or actions the agent is authorized to undertake. For instance, the POA could grant authority over financial matters, real estate transactions, healthcare decisions, or legal proceedings.
- Specify the Duration of the POA: Determine the effective period of the POA. It can be a specific timeframe, such as a year or until a certain event occurs, or it can be a continuous power until revoked by the principal.
- Consider Special Conditions: Include any specific conditions or limitations on the agent’s authority. This could include requiring the agent to provide regular reports, seeking the principal’s consent for certain actions, or setting a limit on the agent’s financial authority.
- Proper Execution and Witnessing: The POA must be properly executed according to KAR US law. This typically involves the principal signing the document in the presence of a notary public or other authorized witness. The witness must also sign the document, confirming the principal’s signature and their understanding of the document’s contents.
- Record and File the POA: In some cases, it may be beneficial to record the POA with the appropriate government agency, such as the county recorder’s office. This can provide public notice of the POA and help prevent disputes or challenges to its validity.
Checklist for Creating a POA in KAR US
A comprehensive checklist can help ensure that all necessary elements are included in the POA, making it legally valid and enforceable.
- Principal Information:
- Full legal name of the principal
- Current address of the principal
- Date of birth of the principal
- Contact information for the principal
- Agent Information:
- Full legal name of the agent
- Current address of the agent
- Date of birth of the agent
- Contact information for the agent
- Scope of Authority:
- Clearly defined powers and limitations of the agent
- Specific transactions, decisions, or actions the agent is authorized to undertake
- Any restrictions or limitations on the agent’s authority
- Duration of the POA:
- Effective date of the POA
- Expiration date of the POA, if applicable
- Conditions for termination of the POA, if any
- Special Conditions:
- Any specific conditions or limitations on the agent’s authority
- Requirements for reporting or obtaining the principal’s consent
- Limits on the agent’s financial authority
- Execution and Witnessing:
- Signature of the principal
- Signature of a notary public or other authorized witness
- Date of execution
- Recording and Filing:
- Information about recording or filing the POA, if applicable
- Name of the government agency where the POA is recorded
- Recording or filing date
Importance of Choosing the Right Attorney for Drafting a POA in KAR US
Selecting an experienced and qualified attorney to draft the POA is crucial. A competent attorney can ensure that the document is legally sound, protects the principal’s interests, and avoids potential complications or disputes.
- Expertise in Estate Planning and Power of Attorney Law: The attorney should have a strong understanding of KAR US laws related to estate planning and power of attorney, including the specific requirements for creating and executing a valid POA.
- Understanding of the Principal’s Needs and Goals: The attorney should carefully listen to the principal’s needs and goals to ensure that the POA accurately reflects their wishes and intentions. This involves understanding the principal’s current circumstances, potential future needs, and their desired level of control over their affairs.
- Clear Communication and Explanation: The attorney should clearly explain the terms and implications of the POA to both the principal and the agent, ensuring that they fully understand the document’s contents and the responsibilities involved.
- Experience in Drafting Legal Documents: The attorney should have experience in drafting legal documents, including POAs, ensuring that the document is well-written, organized, and free from ambiguities or inconsistencies.
Tips for Ensuring the POA is Legally Valid and Enforceable in KAR US
To ensure that the POA is legally valid and enforceable, consider these additional tips:
- Use a Standard POA Form: Utilizing a standard POA form approved by the KAR US government or a reputable legal organization can help ensure that the document meets the necessary legal requirements.
- Review the POA Thoroughly: Before signing the POA, both the principal and the agent should carefully review the document to ensure that they understand its contents and agree with its terms. This includes reviewing the scope of authority, the duration of the POA, and any special conditions.
- Seek Legal Advice: If there are any doubts or questions about the POA, it’s essential to seek legal advice from an experienced attorney. This can help avoid potential legal complications or disputes.
- Update the POA Regularly: As circumstances change, it’s important to review and update the POA to reflect the principal’s current needs and wishes. This may involve modifying the scope of authority, changing the agent, or adjusting the duration of the POA.
Responsibilities and Powers of the Attorney-in-Fact
The attorney-in-fact, the person appointed by the principal to act on their behalf, has significant responsibilities and powers within the KAR US system. These powers are Artikeld in the power of attorney document and are limited to the specific tasks and decisions authorized by the principal.
Limits of the Attorney-in-Fact’s Authority
The attorney-in-fact’s authority is strictly defined by the power of attorney document. They cannot exceed the scope of the granted powers. The principal can limit the attorney-in-fact’s authority by specifying the actions they are allowed to take, the duration of their authority, and the types of transactions they can handle.
Examples of Specific Actions the Attorney-in-Fact Can Take
- Financial Transactions: The attorney-in-fact may be authorized to manage the principal’s bank accounts, pay bills, invest funds, and handle real estate transactions. For example, they could deposit checks into the principal’s account, pay monthly utilities, invest in stocks or bonds, or sell a property on the principal’s behalf.
- Healthcare Decisions: If the power of attorney document grants healthcare authority, the attorney-in-fact can make decisions about the principal’s medical care, including consenting to treatments, accessing medical records, and making end-of-life decisions.
- Legal Matters: The attorney-in-fact might be empowered to handle legal matters on the principal’s behalf, such as signing legal documents, filing lawsuits, or negotiating settlements. For instance, they could sign a lease agreement, file a claim for insurance benefits, or represent the principal in a small claims court case.
Consequences of Exceeding the Attorney-in-Fact’s Authority
If the attorney-in-fact exceeds the authority granted by the power of attorney document, their actions may be considered invalid. This could lead to legal consequences, including:
- Financial Losses: The principal could face financial losses if the attorney-in-fact makes unauthorized transactions, such as withdrawing money from their account or making investments without permission.
- Legal Disputes: The principal could face legal disputes if the attorney-in-fact enters into agreements or takes actions that are not authorized.
- Criminal Charges: In some cases, exceeding the attorney-in-fact’s authority could lead to criminal charges, such as fraud or embezzlement.
Terminating a Power of Attorney in KAR US

A Power of Attorney (POA) grants another person (the attorney-in-fact) the authority to act on your behalf in financial and legal matters. It is important to understand how to terminate a POA in KAR US, as situations may arise where you need to revoke the authority granted.
Revoking a Power of Attorney
Revoking a POA in KAR US involves formally ending the authority granted to the attorney-in-fact. This can be done through various methods, each with its own implications.
- Written Revocation: The most common and effective way to revoke a POA is through a written revocation document. This document should clearly state your intention to revoke the POA, identify the specific POA being revoked, and be signed and dated by you. You should provide a copy of the revocation document to the attorney-in-fact and any relevant parties, such as banks or financial institutions.
- Oral Revocation: While less common, you can also revoke a POA orally, but it is generally advisable to have written evidence of the revocation. This method is typically used in emergencies or when immediate action is required. However, it is essential to ensure that the revocation is communicated to the attorney-in-fact and any relevant parties.
- Subsequent POA: You can revoke a previous POA by creating a new POA that specifically revokes the earlier one. This method is often used when you want to appoint a new attorney-in-fact or modify the powers granted in the previous POA.
Automatic Termination of a Power of Attorney, Kar us power of attorney
In certain circumstances, a POA may be automatically terminated without the need for a formal revocation.
- Death of the Principal: Upon the death of the principal (the person granting the POA), the POA automatically terminates. The attorney-in-fact loses the authority to act on the principal’s behalf.
- Incapacity of the Principal: If the principal becomes incapacitated, the POA may be terminated, depending on the terms of the POA and the laws of KAR US. For instance, if the POA is specifically limited to situations where the principal is competent, it may become invalid upon incapacity.
- Expiration Date: If the POA has an expiration date, it automatically terminates upon the expiry of that date. It is essential to review the POA document and ensure that it has a clear expiration date.
Tips for Ensuring Legal Validity
To ensure that the termination of a POA is legally valid and effective in KAR US, it is essential to follow these tips:
- Consult with an Attorney: It is always advisable to consult with an attorney to ensure that the revocation of a POA is properly executed and complies with all legal requirements.
- Clear and Concise Language: The revocation document should be clear and concise, stating your intention to revoke the POA unequivocally.
- Proper Signatures and Dates: The revocation document should be signed and dated by you, the principal, and any witnesses required by law.
- Proper Notice: Ensure that the attorney-in-fact and any relevant parties are notified of the revocation.
- Record Keeping: Keep a copy of the revocation document and any other relevant documents related to the POA.
Real-World Applications of Power of Attorney in KAR US: Kar Us Power Of Attorney
Power of attorney (POA) is a legal document that grants someone else the authority to act on your behalf. In KAR US, POA is used in various situations, allowing individuals to manage their affairs even when they are unable to do so themselves.
Financial Management
In cases of illness, travel, or disability, a POA can empower a trusted individual to manage your financial affairs. This includes accessing bank accounts, paying bills, investing, and making other financial decisions. This ensures your financial obligations are met and your assets are protected.
- Paying Bills: The attorney-in-fact can pay your bills, such as utilities, mortgage payments, and credit card bills, ensuring timely payments and avoiding late fees.
- Managing Investments: The attorney-in-fact can manage your investments, including buying and selling stocks, bonds, or real estate, based on your instructions or your financial goals.
- Accessing Bank Accounts: The attorney-in-fact can access your bank accounts, withdraw funds, and deposit money as needed, ensuring you have access to funds for daily expenses.
Healthcare Decisions
A healthcare POA, also known as a medical power of attorney, grants someone the authority to make medical decisions on your behalf if you are unable to do so yourself. This ensures that your wishes are followed regarding medical treatment, even if you are unconscious or incapacitated.
- Treatment Decisions: The attorney-in-fact can make decisions regarding medical treatment, such as surgery, medication, or life support, based on your wishes and preferences.
- End-of-Life Care: The attorney-in-fact can make decisions regarding end-of-life care, such as hospice care or organ donation, based on your wishes and preferences.
Property Management
A POA can be used to manage your property, including selling, renting, or making repairs. This is particularly useful if you are unable to manage your property due to illness, travel, or other circumstances.
- Selling Property: The attorney-in-fact can sell your property, including negotiating with buyers, signing contracts, and completing the sale.
- Renting Property: The attorney-in-fact can rent your property, including screening tenants, signing leases, and collecting rent.
- Making Repairs: The attorney-in-fact can make repairs to your property, including hiring contractors and authorizing expenses.
Summary
Understanding KAR US Power of Attorney is crucial for individuals seeking to protect their legal rights and ensure their wishes are carried out. By navigating the legal framework, choosing the appropriate type of POA, and clearly defining the responsibilities of the attorney-in-fact, individuals can establish a robust legal foundation for their future.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the difference between a general power of attorney and a durable power of attorney?
A general power of attorney grants authority to the attorney-in-fact only while the principal is mentally competent. A durable power of attorney remains in effect even if the principal becomes incapacitated.
Can a power of attorney be revoked?
Yes, a power of attorney can be revoked by the principal at any time, as long as they are mentally competent, by providing written notice to the attorney-in-fact.
What happens if the attorney-in-fact dies?
If the attorney-in-fact dies, the power of attorney is automatically terminated. The principal will need to appoint a new attorney-in-fact.





