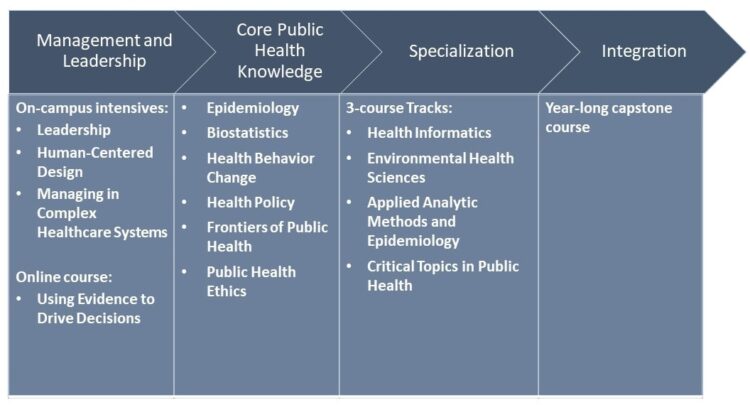
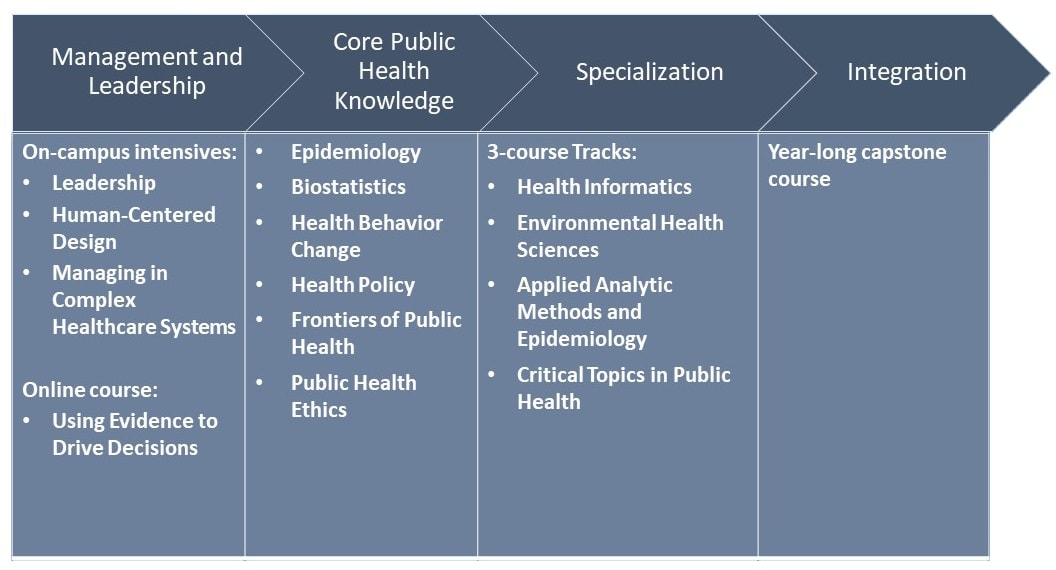
Overview of Public Health Master’s Programs
Public health master’s programs equip individuals with the knowledge, skills, and experience necessary to address complex health issues and improve population health outcomes. They provide a comprehensive understanding of public health principles, methodologies, and practices, empowering graduates to make a significant impact in various settings.
Purpose and Objectives
The primary purpose of public health master’s programs is to prepare graduates for careers in public health practice, research, and policy. They aim to develop:
- A solid foundation in public health core competencies, including epidemiology, biostatistics, environmental health, and health policy.
- Critical thinking and problem-solving skills for addressing public health challenges.
- Leadership and communication abilities for effectively collaborating with diverse stakeholders.
Types of Public Health Master’s Programs
There are various types of public health master’s programs, each with a specific focus and career path:
- Master of Public Health (MPH): A generalist degree providing a broad understanding of public health principles and practices.
- Master of Science in Public Health (MS): A specialized degree focusing on a specific area of public health, such as epidemiology, environmental health, or health policy.
- Master of Health Administration (MHA): A degree designed for individuals interested in management roles in healthcare organizations.
Curriculum and Coursework
Public health master’s programs typically follow a structured curriculum designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of public health principles and practices. The curriculum typically includes core courses, elective courses, and field experience opportunities.
Core Courses
Core courses in public health master’s programs typically cover the foundational concepts and theories of public health, including:
- Biostatistics
- Epidemiology
- Environmental Health
- Social and Behavioral Sciences in Public Health
li>Health Policy and Management
These courses provide students with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify, analyze, and address public health issues effectively.
Elective Courses
In addition to core courses, public health master’s programs offer a wide range of elective courses that allow students to specialize in specific areas of public health, such as:
- Global Health
- Maternal and Child Health
- Occupational Health
- Public Health Nutrition
- Health Communication
Elective courses enable students to tailor their education to their career goals and interests.
Field Experience and Practicums
Field experience and practicums are an essential component of public health master’s programs. These experiences provide students with the opportunity to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world settings. Students may participate in internships, research projects, or community-based initiatives. Field experiences allow students to gain practical experience and develop professional connections that can enhance their career prospects.
Career Opportunities
Graduates of public health master’s programs have a wide range of career opportunities available to them. They can work in a variety of settings, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private businesses.
Some of the most common job titles for public health professionals include:
- Epidemiologist
- Biostatistician
- Health educator
- Environmental health specialist
- Public health administrator
Public health professionals can also work in a variety of industries, including:
- Healthcare
- Education
- Government
- Non-profit organizations
- Private businesses
The earning potential for public health professionals varies depending on their experience, education, and location. However, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for epidemiologists was $76,380 in May 2021.
The job outlook for public health professionals is expected to be good over the next decade. As the population ages and the demand for healthcare services increases, there will be a growing need for public health professionals to help prevent and control diseases.
In addition to the traditional career paths mentioned above, public health graduates also have the opportunity to work in emerging fields such as:
- Global health
- Climate change and health
- Health equity
- Data science for public health
These fields are growing rapidly and offer exciting opportunities for public health professionals to make a difference in the world.
Admissions Requirements and Application Process
Admission to public health master’s programs is generally competitive, and applicants should have a strong academic record and relevant experience. Common admission requirements include:
- A bachelor’s degree in public health or a related field, such as biology, environmental science, or social work.
- A minimum GPA of 3.0 or higher.
- Strong letters of recommendation.
- A personal statement.
- GRE scores (may be required by some programs).
The application process typically involves submitting an online application, transcripts, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement. Deadlines vary by program, but most applications are due in the fall or winter.
To write a strong application essay, applicants should highlight their academic and professional experience, their interest in public health, and their career goals. They should also demonstrate their writing and critical thinking skills.
Funding and Financial Aid
Public health master’s programs offer various financial aid options to assist students in covering the costs of tuition and living expenses.
These options include scholarships, grants, and loans.
Scholarships
Scholarships are merit-based awards that do not require repayment. They are typically awarded based on academic achievement, leadership qualities, or financial need. Many universities offer scholarships specifically for public health students.
Grants
Grants are also awarded based on financial need. Unlike scholarships, grants do not need to be repaid. Federal and state governments, as well as private organizations, offer grants to public health students.
Loans
Loans are borrowed money that must be repaid with interest. Federal student loans are available to all students, regardless of financial need. Private student loans are also available, but they typically have higher interest rates than federal loans.
Applying for Financial Aid
To apply for financial aid, students must complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). The FAFSA is used to determine a student’s eligibility for federal and state grants and loans. Students may also need to complete additional forms required by their university.
Program Rankings and Accreditation
Public health master’s programs vary in quality and reputation. To help prospective students make informed decisions, various organizations and publications rank these programs based on factors such as faculty, research, and career outcomes. These rankings can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of different programs.
Program Accreditation
Accreditation is a formal recognition that a public health program meets certain quality standards. It ensures that the program provides a rigorous curriculum, qualified faculty, and adequate resources to prepare students for professional practice. Accreditation is essential for graduates who wish to work in certain settings, such as government agencies or healthcare organizations.
Accrediting Bodies
Several organizations accredit public health programs, including:
– Council on Education for Public Health (CEPH)
– Public Health Accreditation Board (PHAB)
– Association of Schools and Programs of Public Health (ASPPH)
Online and Distance Learning Programs
Online and distance learning programs offer a flexible and convenient way to earn a public health master’s degree. These programs are designed for students who may not be able to attend traditional on-campus classes due to work, family, or other commitments.
Online programs typically use a combination of online coursework, discussion boards, and video conferencing to deliver content. Distance learning programs may also include some on-campus requirements, such as residencies or internships.
Benefits of Online and Distance Learning Programs
There are several benefits to pursuing an online or distance learning public health master’s program, including:
- Flexibility: Online programs allow students to complete coursework at their own pace and on their own schedule.
- Convenience: Students can access course materials and complete assignments from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Affordability: Online programs are often more affordable than traditional on-campus programs.
- Access to a wider range of programs: Online programs may offer a wider range of courses and programs than traditional on-campus programs.
Challenges of Online and Distance Learning Programs
There are also some challenges to consider when pursuing an online or distance learning public health master’s program, including:
- Lack of face-to-face interaction: Online programs lack the face-to-face interaction that is typically found in traditional on-campus programs.
- Technical difficulties: Students may experience technical difficulties with online coursework, such as slow internet speeds or software issues.
- Time management: Students need to be able to manage their time effectively in order to succeed in an online program.
- Self-motivation: Students need to be self-motivated in order to complete an online program.
Accredited Online and Distance Learning Programs
There are a number of accredited online and distance learning public health master’s programs available. Some of the most popular programs include:
- Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Gillings School of Global Public Health
- University of Michigan School of Public Health
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
- Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Application Process and Admission Requirements for Online Programs
The application process and admission requirements for online public health master’s programs vary from school to school. However, most programs require applicants to have a bachelor’s degree in a related field, such as public health, health sciences, or social sciences. Applicants may also be required to submit GRE scores, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement.