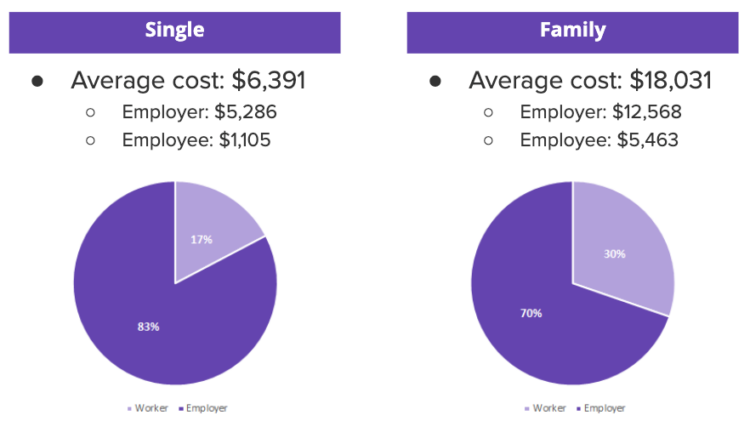
Small Business Health Insurance Cost Components
The cost of health insurance for small businesses is influenced by several key factors, including employee demographics, plan design, and carrier fees.
Employee demographics, such as age, gender, and health status, can impact the cost of health insurance. Older employees and those with pre-existing conditions typically have higher healthcare costs, which can drive up the cost of health insurance premiums for the entire group.
Plan Design
The design of the health insurance plan can also affect the cost. Plans with higher deductibles and co-pays typically have lower premiums, while plans with lower deductibles and co-pays typically have higher premiums.
Carrier Fees
The fees charged by the health insurance carrier can also impact the cost of health insurance. Some carriers have higher administrative costs than others, which can lead to higher premiums for small businesses.
The cost of health insurance for small businesses can also vary based on business size and industry. Smaller businesses typically have higher health insurance costs per employee than larger businesses. This is because smaller businesses have less bargaining power with health insurance carriers and are more likely to be charged higher premiums.
Businesses in certain industries, such as construction and manufacturing, also tend to have higher health insurance costs than businesses in other industries. This is because employees in these industries are more likely to have hazardous jobs and higher rates of injury and illness.
Cost-Saving Strategies for Small Businesses
Small businesses can mitigate health insurance costs through strategic planning and optimization. This section explores effective cost-saving strategies, including plan design optimization, wellness programs, and provider negotiations.
Plan Design Optimization
Modifying plan design parameters can significantly impact premiums. Consider the following strategies:
- Increase Deductibles and Copayments: Higher deductibles and copayments shift more costs to employees, reducing premiums.
- Narrow Provider Networks: Limiting the number of providers within the plan’s network reduces healthcare expenses and premiums.
- Tiered Benefit Plans: Establishing tiers of coverage based on cost-sharing can encourage employees to choose lower-cost options.
Wellness Programs
Investing in employee wellness programs can yield long-term cost savings by promoting preventive care and reducing healthcare utilization. Consider implementing:
- Health Screenings and Immunizations: Regular check-ups and vaccinations can detect and prevent health issues, reducing future healthcare costs.
- Wellness Challenges and Incentives: Competitions and rewards can encourage employees to adopt healthier habits, leading to lower healthcare expenses.
- Smoking Cessation Programs: Smoking-related illnesses are costly. Offering cessation programs can reduce these expenses.
Provider Negotiations
Negotiating with healthcare providers can secure more favorable rates and services. Consider the following tactics:
- Request Competitive Bids: Obtain quotes from multiple providers to compare costs and services.
- Form Provider Alliances: Collaborating with other small businesses to form a purchasing group can increase bargaining power.
- Leverage Data: Analyze claims data to identify high-cost providers and negotiate better rates.
Comparison of Small Business Health Insurance Plans
Small businesses face a wide range of health insurance plan options, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Understanding the key features and costs of these plans is crucial for making informed decisions that meet the needs of the business and its employees.
Plan Types
There are three main types of health insurance plans available to small businesses:
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): Offers a network of providers with negotiated rates, allowing for flexibility in choosing doctors and hospitals. Deductibles and out-of-pocket costs vary.
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): Requires members to use a designated network of providers and primary care physician for most services. Premiums are typically lower than PPOs, but there is less flexibility in choice of providers.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): Similar to HMOs, EPOs restrict members to a specific network of providers but do not require a primary care physician. Premiums are often lower than PPOs, but there is even less flexibility in choosing providers.
Key Features Comparison
The following table Artikels the key features of each plan type to help businesses compare and choose:
| Feature | PPO | HMO | EPO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider Network | Network of providers with negotiated rates | Designated network of providers | Specific network of providers |
| Flexibility | Flexible, can choose any provider in network | Less flexible, must use designated providers | Even less flexible, no choice of providers |
| Deductibles | Varies depending on plan | Typically lower than PPOs | Often lower than PPOs |
| Out-of-Pocket Costs | Higher than HMOs, lower than EPOs | Lower than PPOs, higher than EPOs | Lowest among the three plan types |
| Premiums | Typically higher than HMOs, lower than EPOs | Typically lower than PPOs, higher than EPOs | Lowest among the three plan types |
Pros and Cons
Each plan type has its own advantages and disadvantages:
PPOs:
- Pros: Flexibility in choosing providers, lower out-of-pocket costs than EPOs.
- Cons: Higher premiums than HMOs and EPOs.
HMOs:
- Pros: Lower premiums than PPOs and EPOs, lower out-of-pocket costs than PPOs.
- Cons: Less flexibility in choosing providers, may require referrals for specialists.
EPOs:
- Pros: Lowest premiums among the three plan types, lowest out-of-pocket costs.
- Cons: Even less flexibility in choosing providers than HMOs, no choice of providers outside of network.
By carefully considering the features, costs, and pros and cons of each plan type, small businesses can make informed decisions that meet the specific needs of their employees and budget.
Impact of Health Insurance Costs on Small Business Growth
Health insurance costs can have a significant impact on small business growth. The financial burden of providing health insurance to employees can strain a company’s budget, limit its ability to invest in other areas, and make it difficult to attract and retain top talent.
According to a survey by the Kaiser Family Foundation, the average annual cost of employer-sponsored health insurance for a small business with 10 to 24 employees is $20,000. For businesses with 50 to 99 employees, the average cost is $27,000. These costs can be a major drain on a small business’s resources, especially if the business is not profitable.
Operational Challenges
In addition to the financial burden, health insurance costs can also create operational challenges for small businesses. The administrative tasks associated with managing health insurance can be time-consuming and complex, taking away from the time that business owners could be spending on other tasks.
Small businesses may also face challenges in finding affordable health insurance plans that meet the needs of their employees. Many small businesses are forced to choose plans with high deductibles and co-pays, which can make it difficult for employees to access the care they need.
Strategies for Mitigating Impacts
There are a number of strategies that small businesses can use to mitigate the impact of health insurance costs on their growth.
- Shop around for the best rates. There are a number of different health insurance providers, and it’s important to compare rates from multiple providers before making a decision.
- Consider a group plan. If you have at least 50 employees, you may be eligible for a group health insurance plan. Group plans can offer lower rates than individual plans.
- Offer a high-deductible plan with a health savings account (HSA). HSAs allow employees to save money for medical expenses on a tax-free basis.
- Encourage employees to participate in wellness programs. Wellness programs can help employees stay healthy and reduce the cost of health care.
- Work with a broker. A broker can help you find the best health insurance plan for your business and negotiate the best rates.
By implementing these strategies, small businesses can reduce the impact of health insurance costs on their growth and ensure their long-term success.
Best Practices for Managing Small Business Health Insurance
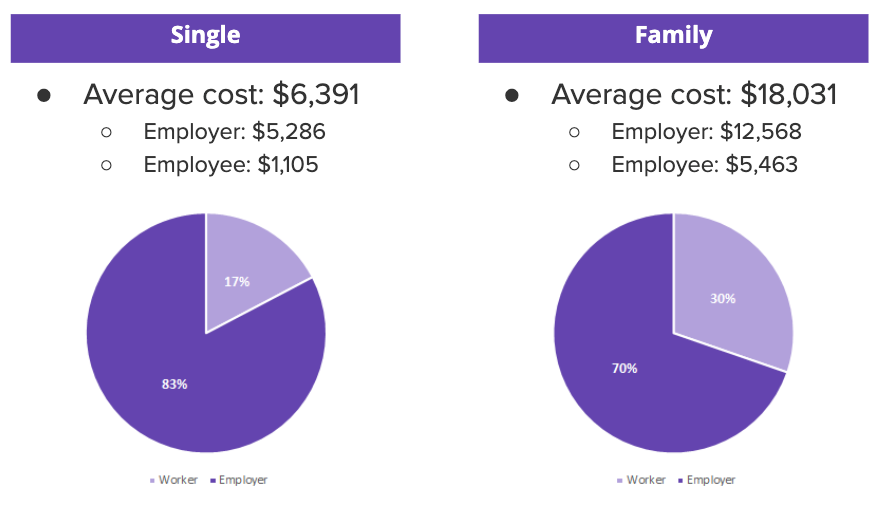
Effectively managing small business health insurance requires a comprehensive approach. This involves selecting the right plan, streamlining enrollment, and efficiently processing claims. By implementing best practices, small businesses can optimize their health insurance programs, control costs, and ensure the well-being of their employees.
Plan Selection
Selecting the optimal health insurance plan is crucial. Consider the following factors:
- Employee demographics: Age, health status, and family size.
- Budget: Determine the amount the business can allocate for health insurance premiums.
- Coverage needs: Identify the essential benefits required by employees, such as doctor visits, hospitalization, and prescription drugs.
Enrollment
Streamlining enrollment ensures that employees are covered promptly. Best practices include:
- Clear communication: Provide employees with comprehensive information about plan options and enrollment procedures.
- Online enrollment: Utilize online platforms for convenient and secure enrollment.
- Employee assistance: Offer support to employees throughout the enrollment process.
Claims Processing
Efficient claims processing minimizes delays and ensures timely reimbursement. Best practices include:
- Dedicated staff: Assign a dedicated team to handle claims processing.
- Automated systems: Implement technology to automate claim submission and tracking.
- Regular audits: Conduct regular audits to identify and rectify any errors or inefficiencies.
Role of Brokers and Technology
Brokers and technology play a vital role in streamlining health insurance management:
- Brokers: Brokers provide expert advice, assist in plan selection, and negotiate favorable rates.
- Technology: Technology automates tasks, improves communication, and enhances claims processing efficiency.