What are insurance companies? Think of them as your financial superheroes, standing ready to protect you from life’s unexpected twists and turns. These companies offer a safety net, providing peace of mind knowing you’re covered in case of emergencies, accidents, or even just plain bad luck. From your car to your health, insurance companies have got you covered – literally!
These companies work by pooling money from individuals and businesses to create a fund that can be used to pay out claims when something unfortunate happens. In exchange for paying premiums, you gain access to financial protection that can help you get back on your feet after a major life event.
Definition and Purpose
Insurance companies are the unsung heroes of the financial world. They provide a safety net for individuals and businesses, helping them navigate life’s uncertainties. Think of them as financial superheroes, ready to swoop in and save the day when disaster strikes.
Definition of Insurance
Insurance is a contract between an individual or entity (the insured) and an insurance company (the insurer). The insured pays a premium to the insurer in exchange for financial protection against potential losses. The insurance company agrees to compensate the insured for covered losses, up to a certain limit, if a specific event occurs.
Types of Insurance Companies, What are insurance companies
Insurance companies come in all shapes and sizes, each specializing in different types of coverage. Here are a few examples:
- Life Insurance Companies: These companies provide financial protection to beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. Think of them as a safety net for loved ones when times are tough.
- Property and Casualty Insurance Companies: These companies offer coverage for damage to property or injuries caused by accidents, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events. Think of them as your shield against the unexpected.
- Health Insurance Companies: These companies provide coverage for medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription drugs. Think of them as your healthcare guardian angel, ensuring you receive the best possible medical care.
Purpose of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies play a vital role in the financial ecosystem. They provide financial security and stability by:
- Transferring Risk: Insurance companies act as risk managers, taking on the financial burden of potential losses from individuals and businesses. This allows individuals and businesses to focus on their goals without worrying about the financial impact of unexpected events.
- Providing Financial Protection: Insurance policies provide financial protection against a wide range of risks, from death and illness to property damage and liability. This protection helps individuals and businesses recover from financial setbacks and avoid catastrophic losses.
- Promoting Economic Stability: Insurance companies contribute to economic stability by providing financial compensation for losses, which helps to mitigate the economic impact of disasters and other unforeseen events. Think of them as the glue that holds the economy together during times of crisis.
Key Functions and Operations
Insurance companies are the unsung heroes of financial stability, offering a safety net for individuals and businesses against unforeseen risks. They play a crucial role in protecting people and assets from potential losses, ensuring peace of mind and financial security. But how do they do it?
Underwriting and Risk Assessment
Underwriting is the process of evaluating the risk associated with insuring a potential policyholder. Insurance companies use a rigorous process to determine the likelihood of a claim and the potential cost. This involves gathering information about the individual or business, their assets, and their history.
The risk assessment process considers several factors, including:
- Age and Health: For health insurance, age and health history are crucial in assessing the risk of future health problems. Younger and healthier individuals typically have lower premiums.
- Driving History: For auto insurance, past driving records, including accidents and traffic violations, play a significant role in determining risk. Drivers with a clean record typically pay lower premiums.
- Credit Score: Credit history can reflect an individual’s financial responsibility, which can be a factor in assessing risk for certain types of insurance, such as auto and homeowners insurance.
- Location: Geographic location can influence risk. For example, areas prone to natural disasters, like hurricanes or earthquakes, may have higher insurance premiums.
- Property Value: For homeowners insurance, the value of the property and its location are key factors in determining the risk of damage or theft.
Insurance companies use sophisticated statistical models and algorithms to analyze these factors and determine the likelihood of a claim. Based on this analysis, they decide whether to accept the risk and, if so, what premium to charge.
Premium Management
Insurance premiums are the payments policyholders make to the insurance company in exchange for coverage. These premiums are the lifeblood of the insurance industry, enabling companies to pay claims and cover operating costs.
Premiums are calculated based on several factors, including:
- Type of Coverage: Different types of insurance policies, such as health, auto, or homeowners insurance, have different premium structures based on the risks involved.
- Coverage Limits: The amount of coverage a policyholder chooses, such as the deductible or the maximum payout, affects the premium. Higher coverage limits typically mean higher premiums.
- Risk Assessment: The underwriting process determines the risk associated with a policyholder, and this risk is reflected in the premium. Higher-risk individuals or businesses typically pay higher premiums.
- Market Conditions: Factors such as inflation, interest rates, and competition in the insurance market can also influence premium rates.
Insurance companies use various strategies to manage premiums, including:
- Risk Pooling: Insurance companies pool premiums from a large number of policyholders to cover the costs of claims. This spreads the risk and helps to ensure that there are enough funds to pay claims when they occur.
- Investment Strategies: Insurance companies invest premiums to generate returns, which helps to offset the cost of claims and ensure long-term financial stability.
- Pricing Models: Insurance companies use sophisticated pricing models to determine the optimal premium rates for different types of policies and risk profiles.
Claims Management
Claims management is the process of handling claims filed by policyholders when they experience a covered loss. This involves investigating the claim, determining the extent of the loss, and processing payments.
The claims management process typically involves the following steps:
- Claim Reporting: Policyholders report claims to the insurance company, providing details about the loss and the circumstances surrounding it.
- Claim Investigation: The insurance company investigates the claim to verify the information provided and assess the extent of the loss. This may involve interviewing witnesses, reviewing documentation, and inspecting the property or the individual’s health records.
- Claim Evaluation: The insurance company evaluates the claim to determine whether it is covered under the policy and the amount of the payout. This may involve consulting with experts, such as doctors or engineers, to assess the damage or the injury.
- Claim Payment: If the claim is approved, the insurance company pays the policyholder the agreed-upon amount, either directly or through a third-party provider.
Insurance companies use various strategies to manage claims efficiently and fairly, including:
- Claims Adjusters: Insurance companies employ claims adjusters who are trained to investigate and evaluate claims, ensuring that they are processed fairly and efficiently.
- Claims Technology: Insurance companies are increasingly using technology to streamline the claims process, such as online claim reporting and automated claim processing systems.
- Claims Prevention: Insurance companies invest in claims prevention programs, such as safety training and educational materials, to help reduce the number and severity of claims.
Role of Actuaries
Actuaries are the financial wizards of the insurance industry, using their expertise in mathematics, statistics, and finance to manage risk and price insurance products. They play a crucial role in ensuring the financial stability of insurance companies by:
- Risk Assessment: Actuaries use statistical models to assess the likelihood and potential cost of future claims, which is crucial for setting appropriate premiums and underwriting policies.
- Premium Setting: Actuaries work with underwriters to determine the appropriate premium rates for different types of insurance policies, taking into account factors such as risk, coverage limits, and market conditions.
- Reserve Management: Actuaries manage the reserves that insurance companies hold to cover future claims. They use their expertise to estimate the amount of reserves needed to ensure that the company can meet its financial obligations.
- Product Development: Actuaries play a key role in developing new insurance products and services, ensuring that they are financially sound and meet the needs of the market.
Types of Insurance Products

Insurance products are like the superhero squad of financial protection, each with its own unique power to shield you from life’s unexpected punches. They come in various forms, each designed to cover a specific risk or need. Let’s dive into the world of insurance and explore the different types available.
Types of Insurance Products
Insurance products can be broadly classified based on the type of risk they cover. Here’s a table summarizing some of the most common types of insurance products:
| Type of Insurance | Description | Main Features | Target Audience |
|—|—|—|—|
| Life Insurance | Provides financial protection to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death. | – Death benefit paid to beneficiaries – Various types, including term, whole life, and universal life – Premium payments can be fixed or variable | Individuals with dependents, those wanting to ensure financial security for loved ones, and those seeking estate planning solutions. |
| Health Insurance | Covers medical expenses, including hospitalization, surgery, and doctor’s visits. | – Coverage for medical services, including preventive care – Different plan options with varying coverage and costs – May include deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance | Individuals, families, and businesses seeking protection against high healthcare costs. |
| Property Insurance | Protects against damage or loss to property, such as homes, cars, and businesses. | – Coverage for damage or loss caused by perils like fire, theft, or natural disasters – Different coverage options, including comprehensive and collision – May include deductibles and limits | Homeowners, car owners, businesses, and landlords. |
| Liability Insurance | Protects against financial losses resulting from legal liability due to negligence or accidents. | – Coverage for legal expenses and damages awarded in lawsuits – Different types, including personal liability, professional liability, and product liability – May have coverage limits and exclusions | Individuals, businesses, and professionals seeking protection against lawsuits and claims. |
| Auto Insurance | Provides coverage for damage to vehicles, injuries to others, and legal liabilities arising from car accidents. | – Coverage for damage to the insured’s vehicle – Liability coverage for injuries to others – Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage – May include deductibles and limits | Car owners and drivers seeking protection against financial losses resulting from accidents. |
| Disability Insurance | Provides income replacement in case of a disability that prevents the insured from working. | – Coverage for a portion of lost income – Different benefit periods and eligibility requirements – May include waiting periods and limitations | Individuals, families, and businesses seeking protection against income loss due to disability. |
| Travel Insurance | Covers expenses related to travel, such as medical emergencies, flight delays, and lost luggage. | – Coverage for medical expenses incurred while traveling – Trip cancellation and interruption coverage – Lost luggage and personal belongings coverage | Travelers seeking protection against unexpected travel-related expenses and disruptions. |
Financial Structure and Regulation

Insurance companies are like the superheroes of the financial world, protecting us from unexpected events. But just like superheroes, they need a strong foundation to operate effectively. This foundation involves their financial structure and the regulatory frameworks that keep them accountable.
Capital and Reserves
Insurance companies need a hefty amount of capital to cover their potential liabilities. This capital acts as a safety net, ensuring they can pay out claims even during tough times. Think of it like a superhero’s secret stash of gadgets – it’s there for when things get really tough. Reserves are another important part of their financial structure. These funds are set aside to cover future claims and expenses. It’s like a superhero’s emergency fund, ensuring they can always stay one step ahead.
Regulatory Frameworks
Insurance companies are heavily regulated to protect policyholders and maintain financial stability. These regulations ensure they operate fairly, transparently, and responsibly. It’s like a team of superheroes working together to ensure everyone’s safety.
Regulatory Landscape Across Countries
The regulatory landscape for insurance companies varies across countries. Some countries have a more hands-off approach, while others have strict regulations. For example, in the United States, insurance companies are regulated at both the state and federal level. This means they have to comply with a complex web of rules.
It’s like a game of international insurance tag, where each country has its own set of rules.
Role in Society and Economy
Insurance companies play a crucial role in society by providing financial security and mitigating risks, ultimately contributing to the stability and growth of national economies. They act as a safety net for individuals and businesses, protecting them from unforeseen events and fostering a sense of confidence in the future.
Social Impact of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies provide financial security to individuals and families by offering protection against various risks. They offer peace of mind knowing that they will be compensated for losses incurred due to unexpected events, such as accidents, illnesses, or natural disasters. This financial security allows individuals to focus on their well-being and future planning without worrying about catastrophic financial burdens.
- Risk Mitigation: Insurance companies mitigate risk by pooling resources from a large group of individuals and businesses. This pooling mechanism allows for the distribution of losses among a wider population, reducing the financial impact on any single individual or entity. By transferring risk from individuals to the insurance company, insurance allows for a more predictable and stable financial environment.
- Financial Security: Insurance provides a safety net for individuals and businesses, ensuring financial stability in the face of unforeseen events. This financial security enables individuals to plan for their future with greater confidence, knowing that they are protected from potential financial setbacks. Insurance companies also contribute to financial security by offering various products and services that meet the specific needs of different individuals and businesses.
- Social Benefits: Insurance companies contribute to society by providing essential services that promote public safety and well-being. For example, health insurance allows individuals to access healthcare services without financial strain, contributing to a healthier population. Similarly, life insurance provides financial support to families in the event of the death of a loved one, ensuring their financial stability and well-being.
Economic Contributions of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies contribute significantly to national economies by providing employment opportunities, generating revenue, and stimulating investment. Their operations involve a wide range of activities, from underwriting and claims processing to investment management and asset allocation, contributing to economic growth and development.
- Employment: Insurance companies employ a large workforce across various sectors, contributing to job creation and economic activity. They provide employment opportunities in areas such as underwriting, claims processing, actuarial science, risk management, and investment management. This employment generation supports families and contributes to overall economic prosperity.
- Revenue Generation: Insurance companies generate significant revenue through premiums paid by policyholders. This revenue contributes to the overall tax base, supporting government services and infrastructure development. Additionally, insurance companies invest a significant portion of their revenue in financial markets, contributing to economic growth and development.
- Investment: Insurance companies play a crucial role in capital formation by investing in various sectors of the economy. They invest in assets such as bonds, stocks, and real estate, providing capital for businesses to grow and expand. These investments contribute to job creation, economic growth, and the development of new technologies and industries.
Relationship with Other Financial Institutions
Insurance companies have close relationships with other financial institutions, such as banks, investment firms, and asset managers. These relationships are essential for the smooth operation of the financial system and the efficient allocation of capital.
- Banking Partnerships: Insurance companies often partner with banks to offer bundled products and services, such as insurance and banking accounts. These partnerships provide convenience and cost savings for customers, while also creating opportunities for both institutions to expand their customer base and generate revenue.
- Investment Management: Insurance companies invest a significant portion of their assets in financial markets, relying on investment firms and asset managers for expertise in portfolio management. These relationships ensure that insurance companies can generate returns on their investments while managing risk effectively.
- Reinsurance: Insurance companies often purchase reinsurance from other insurance companies to mitigate their own risk exposure. This reinsurance market allows insurance companies to share risk and manage their capital requirements more effectively, ensuring financial stability and continuity of operations.
Challenges and Future Trends
The insurance industry, like any other, faces a constantly evolving landscape, with new challenges and opportunities emerging regularly. From the impact of technology to changing customer expectations, insurance companies must adapt to stay ahead of the curve. Let’s dive into the major challenges and explore the future trends shaping the industry.
Technological Advancements Impact
Technological advancements are transforming the insurance industry, creating both opportunities and challenges. These innovations are reshaping how insurance is bought, sold, and delivered.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is revolutionizing insurance operations. AI-powered chatbots are handling customer inquiries, algorithms are assessing risk, and fraud detection systems are becoming more sophisticated. Companies are leveraging AI to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and personalize customer experiences. Think of it like a super-powered insurance assistant that’s always learning and getting smarter.
- Big Data Analytics: Big data analytics enables insurance companies to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, market trends, and risk factors. This data-driven approach helps them develop more personalized products, tailor pricing strategies, and optimize operations. Imagine having a crystal ball that predicts the future of insurance needs, based on a ton of information.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT is connecting devices and collecting real-time data, providing valuable insights into risk assessment and claims management. For example, smart home devices can track usage patterns and detect potential hazards, while telematics devices in vehicles can monitor driving behavior and provide discounts for safe drivers. It’s like having a network of sensors that keep an eye on everything, from your home to your car.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
The insurance industry is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging that are shaping the future of the sector.
- Insurtech: Insurtech refers to the use of technology to disrupt traditional insurance practices. Startups are using innovative approaches to provide faster, more efficient, and customer-centric insurance solutions. Think of it as a fresh perspective on insurance, using technology to make it easier and more accessible.
- Personalized Insurance: The rise of data analytics and AI is enabling insurance companies to offer more personalized products and services. Customers are demanding tailored solutions that meet their specific needs and risk profiles. It’s like having an insurance plan that’s custom-made for you, based on your unique circumstances.
- Digital Transformation: Insurance companies are undergoing a digital transformation, moving away from traditional paper-based processes and embracing digital channels. This shift involves adopting cloud computing, mobile apps, and online platforms to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. Imagine a world where all your insurance needs can be managed from your smartphone, without any paperwork.
Final Review: What Are Insurance Companies
So, next time you think about insurance, don’t just see it as a necessary evil. See it as a smart investment in your future. With a little research and the right insurance plan, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from the unexpected, and sleep soundly knowing you’re prepared for whatever life throws your way.
Helpful Answers
What are some common types of insurance?
There are tons! Some of the most popular include health insurance, life insurance, car insurance, home insurance, and even pet insurance.
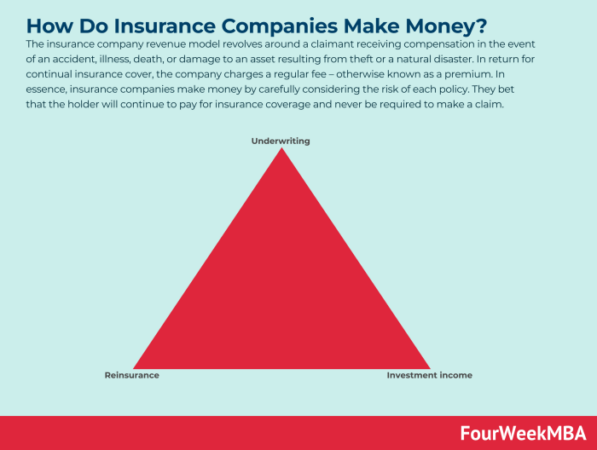
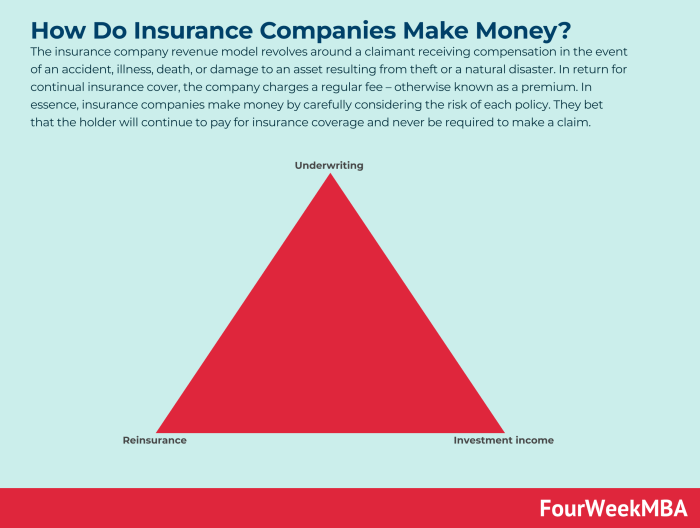
How do insurance companies make money?
They collect premiums from policyholders and invest those funds. When claims are filed, they use those investments to pay out the claims. They also make money from the interest earned on those investments.
Are insurance companies regulated?
Absolutely! They are regulated by state and federal governments to ensure they are financially sound and operating fairly.
Can I choose any insurance company I want?
Yes, you can shop around and compare different companies and policies to find the best fit for your needs and budget.